Questions
Consider the circuit shown in (Figure 1) . Suppose that E = 15 V
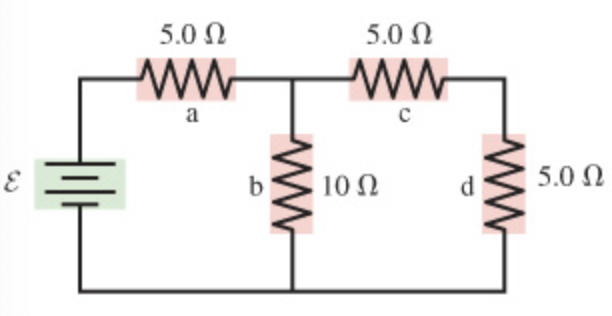
Consider the circuit shown in (Figure 1). Suppose that E = 15 V . include units with answers.
Part A: Find the current through the resistor a.
Part B: Find the potential difference across the resistor a. answer: 7.5 V
Part C: Find the current through the resistor b.
Part D: Find the potential difference across the resistor b.
Part E: Find the current through the resistor c.
Part F: Find the potential difference across the resistor c.
Part G: Find the current through the resistor d.
Part H: Find the potential difference across the resistor d.
In: Physics
Consider the circuit shown in (Figure 1) . Suppose that E = 15 V . include...
Consider the circuit shown in (Figure 1) . Suppose that E = 15 V . include units with answers.
Part A: Find the current through the resistor a.
Part B: Find the potential difference across the resistor a. answer: 7.5 V
Part C: Find the current through the resistor b.
Part D: Find the potential difference across the resistor b.
Part E: Find the current through the resistor c.
Part F: Find the potential difference across the resistor c.
Part G: Find the current through the resistor d.
Part H: Find the potential difference across the resistor d.

In: Physics
A doll sold for ?$215 in 1975 and was sold again in 1989 for $488. Assume...
A doll sold for ?$215 in 1975 and was sold again in 1989 for $488. Assume that the growth in the value V of the? collector's item was exponential.
?a) Find the value k of the exponential growth rate. Assume Vo=215.
?(Round to the nearest? thousandth.)
?b) Find the exponential growth function in terms of? t, where t is the number of years since 1975
?V(t)=
?c) Estimate the value of the doll in 2015.
?(Round to the nearest? dollar.)
?d) What is the doubling time for the value of the doll to the nearest tenth of a? year?
?(Round to the nearest? tenth.)
?e) Find the amount of time after which the value of the doll will be ?$3037
?(Round to the nearest? tenth.)
In: Math
14f) Fill in the blanks with the best possible answer listed One way countries try to...
14f) Fill in the blanks with the best possible answer listed
One way countries try to get out of debt is to Monetize their Debt. This Involves Increasing_________(Q, M, V, P) which Increases_________(Q, M, V, P). This effectively transfers wealth from the Citizens to the Government and also from_________(Debtors, Lenders) to_________(Debtors, Lenders).
In the long-term this hurts GDP growth as it decreases trust in the Government________(True, False). If you have a home loan or a car loan should you repay the loan quickly if you think Inflation is coming?___________(Yes, No). (Assuming you have no job concerns)
In: Economics
Question 6 – 8 refer to prospect H and K below ? = ($100, 0.4; $200,...
Question 6 – 8 refer to prospect H and K below
? = ($100, 0.4; $200, 0.6) ? = ($120, ?; $300, 1 − ?)
6. ?V(?) = ?V(?). What value of p makes this statement true?
7. Carol owns prospect H and is interested in selling it. Her utility of wealth function is given by ?(?) = ?^0.5. What is the lowest price for which Carol would be willing to sell prospect H?
8. True or False: The lowest value of K is greater than the lowest value of H, and the highest value of K is greater than the highest value of H, so everyone – regardless of risk preferences – will prefer K to H.
In: Economics
The fluoride ISE is used routinely for measuring fluoridated water and fluoride ion in dental products...
The fluoride ISE is used routinely for measuring fluoridated water and fluoride ion in dental products such as mouthwash. A 50 mL aliquot of water containing sodium fluoride is analyzed using a fluoride ion electrode and the MSAs. The pH and ionic strength are adjusted so that all fluoride ion is present as free F- ion. The potential of the ISE/reference electrode combination in a 50 mL aliquot of the water was -0.1805 V. Addition of 0.5 mL of a 100 mg/L F- ion standard solution to the beaker changed the potential to -0.3490 V. Calculate the concentration of (1) fluoride ion and (2) sodium fluoride in the water sample.
In: Chemistry
NASA is sending a remote-sensing spacecraft to Mars. Given: Earth parking orbit altitude= 1000 km Mars...
NASA is sending a remote-sensing spacecraft to Mars.
Given:
Earth parking orbit altitude= 1000 km
Mars Parking orbit altitude= 500 km
μEarth = 3.99x105 km3/s2
μMars = 4.280x104 km3/s2
μSun = 1.33x1011 km3/s2
Earth's orbital radius = 1.50 x108 km (assume Earth has a circular orbit for this problem)
Mars' orbital radius = 2.28 x108 km (assume Mars has a circular orbit for this problem)
Find the semi major axis of the transfer orbit, v∞Earth , v∞Mars, ΔVboost,ΔVretro ,ΔVmission (enter your answer as a number which will be assumed to be in km)
In: Mechanical Engineering
During isobaric process m=64 kg of wet water stream at temperature t=262.7?C and pressure p=49 bar...
During isobaric process m=64 kg of wet water stream at temperature t=262.7?C and pressure p=49 bar changed its specific volume from v1 =0.0018 m3/kg to v2=0.035 m3/kg. Find initial and final quality of steam, change of internal energy of steam, work done by steam, amount of heat exchanged with surroundings. Draw the process at the enthalpy-entropy diagram. From tables for p=49 bar: v’=0.0013 m3/kg, v”=0.0403 m3/kg, h’= 1148.4 KJ/kg, h”= 2794.7 KJ/kg
In: Mechanical Engineering
A galvanic (voltaic) cell consists of an electrode composed of nickel in a 1.0 M nickel(II)...
A galvanic (voltaic) cell consists of an electrode composed of nickel in a 1.0 M nickel(II) ion solution and another electrode composed of gold in a 1.0 M gold(III) ion solution, connected by a salt bridge. Calculate the standard potential for this cell at 25 °C.
____V
2)Consider these two entries from a fictional table of standard
reduction potentials.
X2+ + 2e- => X(s) E=2.26 V
Y2+ + 2e- => Y(s) E=0.14 V
Which pair of species would react under standard conditions?
_X2+ and Y
_X2+ and Y2+
_X and Y
_X and Y2+
In: Chemistry
(a) Let λ be a real number. Compute A − λI. (b) Find the eigenvalues of...
(a) Let λ be a real number. Compute A − λI.
(b) Find the eigenvalues of A, that is, find the values of λ for which the matrix A − λI is not invertible. (Hint: There should be exactly 2. Label the larger one λ1 and the smaller λ2.)
(c) Compute the matrices A − λ1I and A − λ2I.
(d) Find the eigenspace associated with λ1, that is the set of all solutions v = v1 v2 to (A − λ1I)v = 0.
(e) Find the eigenspace associated with λ2 similarly.
Repeat the process to find the eigenvalues and corresponding eigenspaces for
A = [ 0 2 0
2 0 0
1 1 4 ]
(Note that this matrix has three eigenvalues, not 2.)
In: Math