Questions
NAD+ -dependent Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate + Dehydrogenase from Thermoproteus tenax. 1. Name the three enzymes that catalyze irreversible,...
NAD+ -dependent Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate + Dehydrogenase from Thermoproteus tenax.
1. Name the three enzymes that catalyze irreversible, regulated reactions in glycolysis as studied in class.
2. What is the significance of the GAPDH reaction in E. coli to glycolysis?
3. How does the reaction catalyzed by GAPDH from T. tenax presented here differ from the reaction carried out in E. coli?
4. The activity of the GAPDH enzyme was assayed in the presence of a constant amount of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and an increasing amount of NAD . The activity of the control was + compared to the activity in the presence of various metabolites. The results are shown in Figure 20.2. Additional data are given in Table 20.2.
a. Use the data in Figure 20.2 to estimate a KM value for the enzyme in the presence of these metabolites. Classify the metabolites listed in Table 20.2 as inhibitors or activators. Fill in your answers in the table provided. Explain how you decided whether these metabolites are inhibitors or activators, based on the graph.
b. How would you classify NADH, ADP and ATP? (These data are not presented in the graph). Are they inhibitors or activators? Add this information to Table 20.2.
c. Explain the physiological significance of your answers to questions 4a and 4b. NAD+ -dependent Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate + Dehyd
5. In the absence of NADP+, the binding of NAD+ to the T. tenax GAPDH showed no cooperative binding (closed circles, Figure 2 above). In the presence of NADP however, the binding of NAD+ to the T. tenax GAPDH was found to have a Hill coefficient of 2 (open circles, Figure 2 above).
a) What is the significance of the change in the value of the Hill coefficient?
b) Is this consistent with the shape of the curve and the information given in the background concerning the enzyme's quaternary structure?
6. What is the ATP yield for one mole of glucose oxidized by the pathway that uses the non-phosphorylating GAPDH enzyme?
In: Biology
Adam and Eve are stranded on a desert island. There are only two goods on the...
Adam and Eve are stranded on a desert island. There are only two goods on the island: Apples (A) and Bananas (B). The utility functions of Adam and Eve are U^Adam(DA, DB) = (DA)^1/2 (DB)^1/2 and U^Eve(DA, DB) = (DA)^1/2 (DB)^1/2 respectively (they have the same preferences). Total endowments on the island are 20 Apples and 60 Bananas. Adam owns all the bananas and Eve all the apples.
(a) Draw the Edgeworth box for this exchange economy, including Adam and Eve’s indifference curves and endowments.
(b) Write the equation of the contract curve of this economy.
(c) Will Adam consume any apple in a competitive equilibrium?
(d) Now assume U^Adam(DA, DB) = U^Eve(DA, DB) = DA + DB. What is the new contract “curve”? (Hint: note the quotation marks and recall the condition that must be satisfied for the contract curve, i.e. MRS for the consumers must be equal.)
In: Economics
Salivary amylase is a digestive enzyme which begins the digestion of ____ Proteins Starch Lipids Glucose...
-
Salivary amylase is a digestive enzyme which begins the digestion of ____
-
Proteins
-
Starch
-
Lipids
-
Glucose
-
Nucleic acids
-
-
The ____ exits directly from the gallbladder
-
Right hepatic duct
-
Left hepatic duct
-
Cystic duct
-
Common bile duct
-
Common hepatic duct
-
-
All of the following are areas of the stomach except ____
-
Cardia
-
Duodenum
-
Fundus
-
Body
-
pylorus
-
-
Mumps is an inflammation and enlargement of the ___
-
Appendix
-
Gallbladder
-
Pancreas
-
Parotid glands
-
tonsils
-
In: Anatomy and Physiology
1. What is activation energy? A. The energy used by the active site to split a...
1. What is activation energy?
| A. The energy used by the active site to split a substrate. |
| B. The energy released when a substrate binds to an active site. |
| C. The energy required to start a metabolic reaction. |
| D. The energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. |
2. Which statement defines your body's metabolic rate?
| A. The speed at which chemical reactions occur when you are resting but awake |
| B. The number of Calories needed to keep your weight stable |
| C. All of the chemical reactions in your body |
| D. A measure of your body’s energy use |
3. Which statement about enzymes is true?
| A. One enzyme can catalyze many different types of reactions for a variety of substrates. |
| B. The shape of an enzyme determines its specificity. |
| C. Enzymes eliminate the activation energy barrier. |
| D. An enzyme molecule is permanently changed by the substrate molecule. |
4. Which reaction occurs during glycolysis?
| A. Glucose is converted into carbon dioxide. |
| B. Glucose is converted into water. |
| C. Glucose is converted into ATP. |
| D. Glucose is converted into pyruvic acid. |
In: Biology
Ribosomes provide the scaffolding on which tRNAs interact with mRNA during translation of an mRNA sequence to a chain of amino acids.
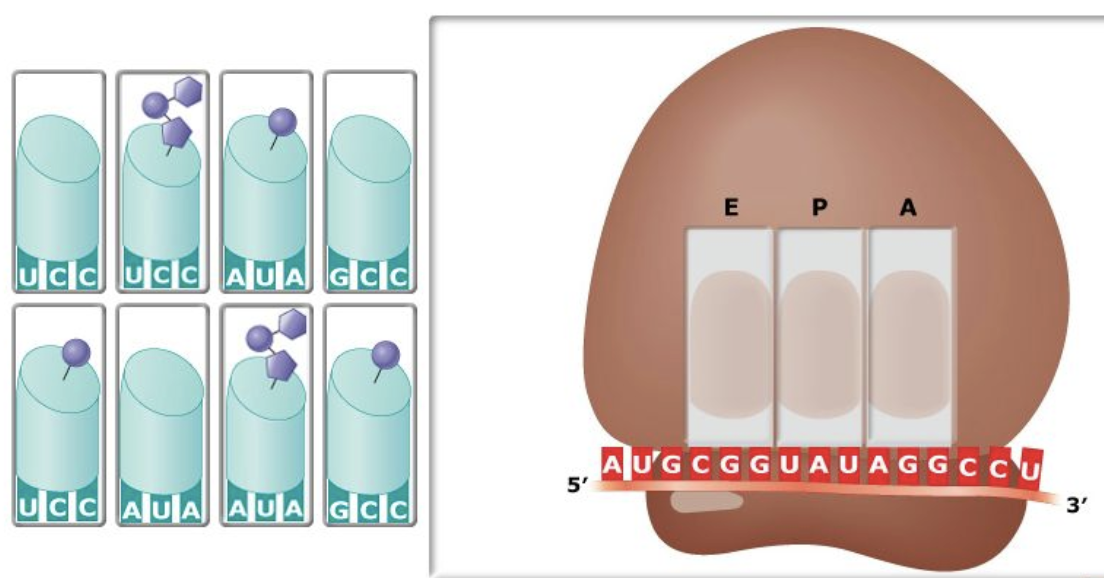
In: Biology
How would the mutation described above, changing a lysine to an arginine alter the histone code...
How would the mutation described above, changing a lysine to an arginine alter the histone code if this lysine was located on the histone tail? What possible effects could this have? Histone proteins are the most conserved proteins of all eukaryotic proteins. That is to say that there is very little variation in the sequence of amino acids from one species to another. Why do you think this is? Please note that this is a 10 point question, please provide ample evidence.
In: Biology
2. Why is it relevant for biochemists to consider the acid/base properties of amino acids? 3....
2. Why is it relevant for biochemists to consider the acid/base properties of amino acids?
3. What are the conventions for displaying a peptide sequence?
4. What chemical characteristic(s) of the peptide bond make it rigid and planar?
5. What are 1-2 concepts you continue to struggle with from the reading?
6. Write one broader question that reading raises for you. This question could relate to applications of concepts to medicine, research, etc
In: Chemistry
Which of the following best describes the tRNA binding sites of the ribosome? Group of answer...
Which of the following best describes the tRNA binding sites of the ribosome?
Group of answer choices
A. The P site contains the tRNA molecule covalently bound to the growing chain of amino acids.
B. All tRNAs leave the ribosome through the A site.
C. Only one of the three sites can be occupied by a tRNA molecule at any given time.
D. Each tRNA that associates with the ribosome must first bind in the P site and then moved to the A site.
In: Biology
1) Explain how the body metabolizes carbohydrates and protein in the fed state. 2) Explain how...
1) Explain how the body metabolizes carbohydrates and protein in the fed state.
2) Explain how the body metabolizes carbohydrates and fat in the fed state.
3) Explain how the body metabolizes carbohydrates and amino acids in the short term fasting states (prior to using up all your glycogen).
4) Explain how the body metabolizes fats in the fasting state once you have used up all your glycogen stores.
In: Biology
What is a codon and how do you identify them in a strand of mRNA? There...
What is a codon and how do you identify them in a strand of mRNA? There are 64 potential codons for only 20 amino acids. Why does this occur? Why is it also important to know the start codon before determining what a codon would be in a given strand of mRNA? After answering this first part, explain the difference between the DNA template and coding strands and explain how each strand relates to the mRNA strand that is produced?
In: Biology