Questions
Answer the following questions related to the given electrochemical cell. 2NO(g) + H2O(l) + 2e− ⇌...
Answer the following questions related to the given electrochemical cell.
2NO(g) + H2O(l) + 2e− ⇌ N2O(g)
+ 2OH−(aq)
E° = 0.760 V
Bi2O3(aq) + 3H2O(l) +
6e− ⇌ 2Bi(s) + 6OH−(aq)
E° = -0.460 V
1. Answer the following questions under standard conditions.
(a) The half cell containing N2O/NO is the (anode /cathode )
(b) The half cell containing Bi2O3/Bi is the (anode/ cathode )
(c) What is E°cell (in V)? Report your answer to three decimal places in standard notation (i.e., 0.123 V).
| Tries 0/3 |
2. One cell compartment is comprised of a Pt electrode in a solution containing NO(g) at a pressure of 0.179 atm and N2O(g) at a pressure of 0.315 atm at a temperature of 356.5 K. The concentration of OH− is 3.68 × 10-4 M.
(a) Choose the appropriate complete Nernst equation below for this half cell.
Remember that molarity and pressure are relative to 1 M and 1 atm, and that solids and liquids have a ratio of 1.
| E = E° + | RT | ln | PNOa |
| nF | PN2Oc |
| E = E° + | RT | ln | PN2Oc[OH−]d |
| nF | PNOa(1)b |
| E = E° + | RT | ln | PNOa(1)b |
| nF | PN2Oc[OH−]d |
| E = E° + | RT | ln | PN2Oc |
| nF | PNOa |
| Tries 0/3 |
(b) What is Ecell (in V) for the N2O/NO half cell? Report your answer to three decimal places in standard notation (i.e., 0.123 V).
| Tries 0/3 |
3. The other cell compartment is comprised of a Pt electrode in a solution containing Bi2O3(aq) at a concentration of 1.76 × 10-1 M and Bi(s) at a temperature of 356.5 K. The concentration of OH− is 8.92 × 10-3 M.
(a) Choose the appropriate complete Nernst equation below for this half cell.
Remember that molarity and pressure are relative to 1 M and 1 atm, and that solids and liquids have a ratio of 1.
| E = E° + | RT | ln | [Bi2O3]a(1)b |
| nF | (1)c[OH−]d |
| E = E° + | RT | ln | (1)c |
| nF | [Bi2O3]a |
| E = E° + | RT | ln | [Bi2O3]a |
| nF | (1)c |
| E = E° + | RT | ln | (1)c[OH−]d |
| nF | [Bi2O3]a(1)b |
| Tries 0/3 |
(b) What is Ecell (in V) for the Bi2O3/Bi half cell? Report your answer to three decimal places in standard notation (i.e., 0.123 V).
| Tries 0/3 |
4. Under the conditions described in questions 2 and 3:
(a) The half cell containing N2O/NO is the (cathode /anode)
(b) The half cell containing Bi2O3/Bi is the (cathode/ anode )
(c) What is Ecell (in V)? Report your answer to three decimal places in standard notation (i.e., 0.123 V).
| Tries 0/3 |
In: Chemistry
I want the code below to be edited: Rather than giving the input string inside the...
I want the code below to be edited:
Rather than giving the input string inside the code, I want the
program to ask the user for an input and calculate and complete
this code.
I have pasted the actual code below, Please edit the input section
only so that I can input any string or any sentence as I like. The
program must ask the user that "Enter a
string/sentence" and take the data to calculate the
Huffman code.
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define MAX_TREE_HT 256
using namespace std;
map<char, string> codes;
map<char, int> freq;
struct MinHeapNode
{
char data;
int freq;
MinHeapNode *left, *right;
MinHeapNode(char data, int freq)
{
left = right = NULL;
this->data = data;
this->freq = freq;
}
};
struct compare
{
bool operator()(MinHeapNode* l, MinHeapNode* r)
{
return (l->freq > r->freq);
}
};
void printCodes(struct MinHeapNode* root, string str)
{
if (!root)
return;
if (root->data != '$')
cout << root->data << ": " << str << "\n";
printCodes(root->left, str + "0");
printCodes(root->right, str + "1");
}
void storeCodes(struct MinHeapNode* root, string str)
{
if (root==NULL)
return;
if (root->data != '$')
codes[root->data]=str;
storeCodes(root->left, str + "0");
storeCodes(root->right, str + "1");
}
priority_queue<MinHeapNode*, vector<MinHeapNode*>, compare> minHeap;
void HuffmanCodes(int size)
{
struct MinHeapNode *left, *right, *top;
for (map<char, int>::iterator v=freq.begin(); v!=freq.end(); v++)
minHeap.push(new MinHeapNode(v->first, v->second));
while (minHeap.size() != 1)
{
left = minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
right = minHeap.top();
minHeap.pop();
top = new MinHeapNode('$', left->freq + right->freq);
top->left = left;
top->right = right;
minHeap.push(top);
}
storeCodes(minHeap.top(), "");
}
void calcFreq(string str, int n)
{
for (int i=0; i<str.size(); i++)
freq[str[i]]++;
}
string decode_file(struct MinHeapNode* root, string s)
{
string ans = "";
struct MinHeapNode* curr = root;
for (int i=0;i<s.size();i++)
{
if (s[i] == '0')
curr = curr->left;
else
curr = curr->right;
if (curr->left==NULL and curr->right==NULL)
{
ans += curr->data;
curr = root;
}
}
return ans+'\0';
}
int main()
{
string str = "Please remove this input and help me put my own input into the program";
string encodedString, decodedString;
calcFreq(str, str.length());
HuffmanCodes(str.length());
cout << "Character With there Frequencies:\n";
for (auto v=codes.begin(); v!=codes.end(); v++)
cout << v->first <<' ' << v->second << endl;
for (auto i: str)
encodedString+=codes[i];
cout << "\nEncoded Huffman data:\n" << encodedString << endl;
decodedString = decode_file(minHeap.top(), encodedString);
cout << "\nDecoded Huffman Data:\n" << decodedString << endl;
return 0;
}In: Computer Science
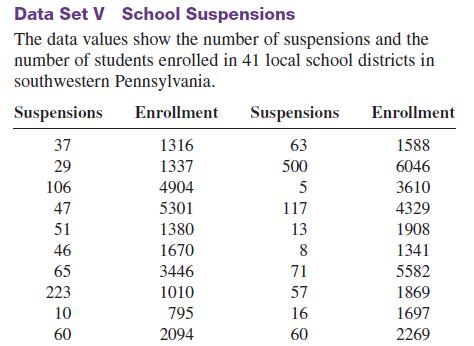
Randomly select 10 values from the number of suspensions in the local school districts in southwestern Pennsylvania in Data Set V in Appendix B.
Randomly select 10 values from the number of suspensions in the local school districts in southwestern Pennsylvania in Data Set V in Appendix B. Find the mean, median, mode, range, variance, and standard deviation of the number of suspensions by using the Pearson coefficient of skewness.
Data from Set V Appendix B
In: Statistics and Probability
Consider a stationary solution of the Schrodinger Equation with positive energy E for a particle with...
Consider a stationary solution of the Schrodinger Equation with positive energy E for a particle with mass m in the following one-dimensional potential: V (x) = 0 for |x| > a and V (x) = −V0 for |x| ≤ a with V0 > 0. (a) Calculate the transmission and reflection probabilities. (b) Show that the transmission probability is unity for some values of the energy.
In: Physics
Suppose that you are designing a parachute so that the terminal velocity using the parachute will...
Suppose that you are designing a parachute so that the terminal velocity using the parachute will be the same as the velocity at the end of a normal (frictionless) jump from a height of 2.80 m. If the parachute exerts a drag force of - b v where v is in meters per second and if the parachute is designed for an 70.0 kg person, what is b?
In: Physics
1. Consider a charge of -1 nC at (-1,0) m, and a charge of +1 nC...
1. Consider a charge of -1 nC at (-1,0) m, and a charge of +1 nC at (1,0). Calculate the electric potential everywhere in the plane.
2. For the same geometry as in the first problem, calculate the electric field everywhere, using -?V =E. In 2 dimensions, ?V= (?subxV, ?subyV) = ?subxV x^ + ?suby Vy^
In: Physics
For the 2 × 2 game, find the optimal strategy for each player. Be sure to...
For the 2 × 2 game, find the optimal strategy for each player. Be sure to check for saddle points before using the formulas.
3 −3 2 3
For row player R:
r1 =
r2 =
For column player C:
c1 =
c2=
Find the value v of the game for row player R.
v =
In: Math
A 15.2% (m/v) solution of sodium chloride (NaCl) is used to prepare 25.0 L of a...
A 15.2% (m/v) solution of sodium chloride (NaCl) is used to prepare 25.0 L of a physiological saline solution with a concentration of 0.154 M NaCl. What volume of the 15.2% (m/V) solution of sodium chloride would be required to make 25.0 L of the physiological saline solution ( 0.154 M NaCl) ?
In: Chemistry
For the following reaction: NiO2(s) + 4 H+(aq) + 2 Ag(s) → Ni2+(aq) + 2 H2O(l)...
For the following reaction: NiO2(s) + 4 H+(aq) + 2 Ag(s) → Ni2+(aq) + 2 H2O(l) + 2 Ag+(aq) script E° = 2.48 V Calculate the pH of the solution if script E = 2.32 V and [Ag+] = [Ni2+] = 0.012 M. Use the Standard Reduction Table.
In: Chemistry
discuss how teachers' expectations of and interactions with students affect students' academic success and sense of...
In: Psychology