Questions
The commercially available pUC57 plasmid is circular with 2710 bp. It has one EcoRI cleavage site...
The commercially available pUC57 plasmid is circular with 2710 bp. It has one EcoRI cleavage site at 396 and one HindIII cleavage site at 471. How many bands would you expect to see on the gel if both enzymes were used to digest the enzyme and the digestion was complete? Explain your answer.
Using the same plasmid and restriction enzymes as in question 2, how many bands would you expect to see on the gel if the digestion were partial? A partial digestion means that
not every site on every molecule is cleaved by the restriction enzyme. Explain your answer
In: Biology
There are a number of mitochondrial disorders that affect people with mutations related to enzymes for...
In: Biology
Acetylcholinesterase catalyzes the hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine: Acetylcholine + H2O acetate + choline The...
Acetylcholinesterase catalyzes the hydrolysis of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine: Acetylcholine + H2O acetate + choline The Km of acetylcholinesterase for its substrate acetylcholine is 9.5x10-5M. In a reaction mixture containing 5 nanomoles/mL of acetylcholinesterase and 150μM acetylcholine, a velocity vo=40μmol/mLsec was observed for the acetylcholinesterase reaction.
a. Calculate Vmax for this amount of enzyme
b. Calculate kcat for acetylcholinesterase
c. Calculate the catalytic efficiency (kcat/Km) for acetylcholinesterase
d. Does acetylcholinesterase approach catalytic perfection?
e. What determines the ultimate speed limit of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction? That is, what is it that imposes the physical limit on catalytic perfection?
In: Biology
A, B, C, D are all matricies A = 2x3 1 2 −3 −1 4 5...
A, B, C, D are all matricies
A = 2x3
1 2 −3
−1 4 5
,
B = 2x3
3 0 −1
1 2 1
, C = 2x2
2 5
1 2
,
D = 3x3
1 −1 1
2 −1 2
4 −3 4
Find each of the following or explain why it does not exist.
1) A + B,
2) 2A − 3B,
3) A + C,
4) A − C,
5) AC,
6) CA,
7) AD,
8) DA,
9) C
10) D−1
.
11) Solve the matrix equation CX = B
In: Math
Write the overall reaction for pyruvate oxidation (for one pyruvate) Write the overall reaction for the...
-
Write the overall reaction for pyruvate oxidation (for one pyruvate)
-
Write the overall reaction for the Citric Acid Cycle (for one acetyl-CoA)
-
What was the overall reaction for glycolysis?
-
Per glucose, how many pyruvate (and then acetyl-CoA) are formed?
-
How many Citric Acid Cycles have to take place to break down the pyruvates from one glucose molecule?
-
Write the overall reaction for pyruvate oxidation (for one glucose)
-
Write the overall reaction for the Citric Acid Cycle (for one glucose)
-
Using the protein complex abbreviations and arrows, write the path of electrons from NADH to oxygen. Circle the places in the process where hydrogen ions are pumped across the membrane.
-
Using the protein complex abbreviations and arrows, write the path of electrons from FADH2 to oxygen. Circle the places in the process where hydrogen ions are pumped across the membrane.
-
NADH molecules from glycolysis must travel into the mitochondria to pass their electrons to the electron transport chain. Because this process takes some energy, for every NADH from glycolysis, 2 ATP are formed, instead of 3. Add up all of the ATPs from each NADH and FADH2 produced during the complete breakdown of one glucose molecule. What is the net ATP gain from one glucose. Show your calculation below.
-
Oxidative phosphorylation cannot occur when there is no oxygen to accept electrons from complex 4. In anaerobic conditions( no or low oxygen), electrons quickly build up in the complexes and have nowhere to go. Interestingly, the citric acid cycle also stops when there is no oxygen.Why? What does the oxidative phosphorylation produce that citric acid cycle needs to continue working?
-
There are several known poisons that are capable of killing humans by inhibiting or stopping oxidative phosphorylation. Research two of them and describe how they affect oxidative phosphorylation below
In: Biology
Which beaker best illustrates what happens when the following acids are dissolved in water?
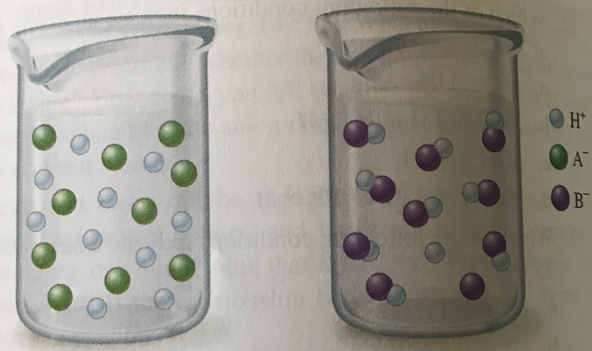
Which beaker best illustrates what happens when the following acids are dissolved in water?
a. HNO2 b. HNO3 c. HCI d. HF e. HC2H3O2
In: Chemistry
1. List eight diet and/or lifestyle practices that can minimize your heart disease risk. 2. Why...
1. List eight diet and/or lifestyle practices that can minimize
your heart disease risk.
2. Why does the body package fatty acids as lipoproteins?
In: Nursing
Regulating Metabolism 1. Fatty acids are broken down into ____________________, which occurs in the ____________________________. 2....
Regulating Metabolism
1. Fatty acids are broken down into ____________________, which occurs in the ____________________________.
2. High concentrations of acetyl-coA indicates _______________ __________________.
3. Pyruvate comes from the breakdown of __________________ and _________________ _________________.
In: Biology
What is the function of pancreatic juice? Group of answer choices a) Stimulates the release of...
What is the function of pancreatic juice?
Group of answer choices
a) Stimulates the release of bicarbonate
b) It "neutralizes" acids
c) Aids in chemical digestion
d) All of the above
In: Anatomy and Physiology
1. the reaction for photosynthesis is like the mirror image of another reaction called A) ATP...
1. the reaction for photosynthesis is like the mirror image of another reaction called
A) ATP hydrolysis
B) redox reaction
C) phosphorylation
D) cellular respiration
2. Photosynthesis consists of which two set of reactions that are linked by redox reactions to generate chemical energy
A) light capturing reactions and splitting water
B) light capturing reactions and chemiosmosis
C) light capturing reactions and Kelvin cycle
D) light capturing reactions and oxidative phosphorylation
3. The photosynthetic pigments of plant are located in or at the
A) cellular cytoplasm
B) thylakoid membrane
C) stroma
D) apoplast
4. To date, in all of biology, only Photosystem II is known to use solar energy to
A) provide highly energetic electrons to redox reactions that generate chemical energy
B) to provide energy for chemiosmosis
C) absorb light of a wavelength between 550 and 600 nm
D) produce oxygen by oxidizing (or splitting) water.
5. Rubisco is
A) the enzyme that fixes CO2 to RuBP
B) a slow enzyme
C) an enzyme that can catalyze two different reactions
D) All of the above
In: Biology