Questions
what was the purpose/hypotheses, basic method, findings, limitations/criticisms, issues, and how can we use the information...
what was the purpose/hypotheses, basic method, findings, limitations/criticisms, issues, and how can we use the information today from the Bobo Doll experiment? What topic in social psychology did it help define?
In: Psychology
Albert Bandura's Bobo Doll experiment changed the way we think about modeling and social learning. In...
Albert Bandura's Bobo Doll experiment changed the way we think about modeling and social learning. In your opinion, do you think that children learn violent behavior from playing video games?
In: Psychology
Define the term “Historical Control” and explain its relevance to issues surrounding the differences between a...
Define the term “Historical Control” and explain its relevance to issues surrounding the differences between a “Randomized Controlled Experiment” and an “Observational Study”.
Explain the difference between a “quantitative variable” and a “qualitative variable” and give an example of each.
In: Math
1- Why do you think some of the indicators used in experiment 2 were different than the ones used in experiment 1?
Experiment 1: Measure the pH of Acids
Lab Results
Record your observations in the table below.
| Test Tube # | Bromothymol Blue Color | Methyl Yellow Color | Bromocresol Green Color |
| 1 | Goldish Yellow | Dark Red | Goldish Yellow |
| 2 | Goldish Yellow | Red | Dark Goldish Yellow |
| 3 | Goldish Yellow | Orange | Much Darker Goldish Yellow |
| 4 | Goldish Yellow | Dark Yellow | Green |
| 5 | Darker Goldish Yellow | Yellow | Blue |
| 6 | Green | Yellow | Darker Blue |
| 7 | Turquize | Lighter Yellow | Much Darker Blue |
Data Analysis
For each test tube, calculate the concentration of H3O and pH. You can use the following formula to determine the concentration of HCl.
M1 x V1 = M2 x V2
where M1 and V1 are the molarity and volume of the first solution and M2 and V2 are the molarity and volume of the second solution.
Given that HCl is a strong acid, the H3O concentration is equal to the HCl concentration except at very low concentrations (test tube 6 and 7) where the H3O from the dissociation of water (1.00*10^-7) becomes significant.
| Test Tube # | HCl Concentration | [H3O] | pH |
| 1 | 0.1 M | 0.1 | 1 |
| 2 | 0.01 M | 0.01 | 2 |
| 3 | 0.001 M | 0.001 | 3 |
| 4 | 0.0001 M | 0.0001 | 4 |
| 5 | 0.00001 M | 0.00001 | 5 |
| 6 | 0.000001 M | 0.000001 | 6 |
| 7 | 0.0000001 M | 0.0000001 | 7 |
Experiment 2: Measure the pH of Bases
Lab Results
Record your observations in the table below.
| Test Tube # | Bromothymol Blue Color | Alizarin Yellow Color | Pheonlphtalein Color |
| 1 | Dark Blue | Dark Red | Dark Purple |
| 2 | Lighter Blue | Redish / Orange | Purple |
| 3 | Blue | Orange | Purple |
| 4 | Blue | Dark Yellow | Purple |
| 5 | Blue | Yellow | Lighter Purple |
| 6 | Blue | Yellow | Transparent |
| 7 | Turquize | Lighter Yellow | Transparent |
Data Analysis
For each test tube, calculate the concentration of NaOH, OH–, H3O, and pH. You can use the following formula to determine the concentration of NaOH.
where M1 and V1 are the molarity and volume of the first solution and M2 and V2 are the molarity and volume of the second solution.
M1 x V1 = M2 x V2
Given that NaOH is a strong base, the HO– concentration is equal to the NaOH concentration except at very low concentrations (test tube 6 and 7) where the HO– from the dissociation of water (1.00*10^-7) becomes significant.
| Test Tube # | NaOH Concentration | [HO–] | [H3O] | pH |
| 1 | ||||
| 2 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 4 | ||||
| 5 | ||||
| 6 | ||||
| 7 |
Conclusion
1- Why do you think some of the indicators used in experiment 2 were different than the ones used in experiment 1?
2- Suppose a student mixed his HCl and NaOH solution and decided to use bromothymol blue to figure out which is which. Which test tube in the figure below contains NaOH?
A: Yellow Test Tube
B: Blue Test Tube
In: Chemistry
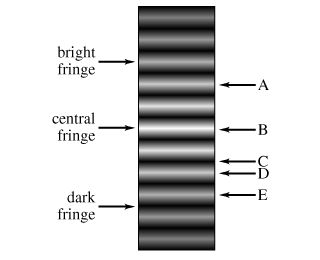
The figure (Intro 1 figure) shows the interference pattern obtainedin a double-slit experiment with light...

|
In: Physics
A double-slit experiment yields an interference pattern due to the path length difference from light traveling...
A double-slit experiment yields an interference pattern due to the path length difference from light traveling through one slit versus the other. Why does a single slit show a diffraction pattern?
A double-slit experiment yields an interference pattern due to the path length difference from light traveling through one slit versus the other. Why does a single slit show a diffraction pattern?
| The single slit must have something in the middle of it, causing it to act like a double slit. | |
| There is a path length difference from waves originating at different parts of the slit. | |
| The wavelength of the light is shorter than the slit. | |
| The light passing through the slit interferes with light that does not pass through. |
In: Physics
The experiment of rolling a fair six-sided die twice and looking at the values of the...
The experiment of rolling a fair six-sided die twice and looking at the values of the faces that are facing up, has the following sample space.
For example, the result (1,2) implies that the face that is up from the first die shows the value 1 and the value of the face that is up from the second die is 2.
sample space of tossing 2 die
A pair of dice is thrown.
Let X = the number of multiples of 2.
Complete the table to construct a probability distribution for X using the sample space from the experiment of rolling two fair six-sided dice.
Note: Your answers should be approximate decimals to 4 places.
|
X |
P(x) |
|
0 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
Probability distribution for X = num. of multiples of
2
In: Statistics and Probability
How many moles of ethane were burnt
240 cm3 of ethane (C2H6) was burnt in a controlled way and found to raise the temperature of 100 cm3 of water by 33.5 °C. (specific heat capacity of water = 4.18Jg–1K–1; 1mol of gas molecules occupies 24.0 dm3 at r.t.p.)
a. How many moles of ethane were burnt?
b. Calculate the heat change for the experiment.
c. Calculate the molar enthalpy change of combustion for ethane, as measured by this experiment.
d. Use the values below to calculate the standard molar enthalpy change for the complete combustion of ethane.
ΔHQf[CO2] = –394 kJ mol–1
ΔHQf[H2O] = –286 kJ mol–1
ΔHQf[C2H6] = –85 kJ mol–1
e. Give possible reasons for the discrepancy between the two results.
In: Chemistry
Question: Write the reaction(s), with the reactant and products' structures to describe the following experiment. In...
Question: Write the reaction(s), with the reactant and products' structures to describe the following experiment.
In this experiment you will steam distill clove oil from freshly ground cloves. Following the distillation, clove oil and water will be present in the receiving flask. Because clove oil will be a minor fraction of the distillate, the clove oil must be extracted from the water into an organic solvent such as dichloromethane. Removing the dicholormethane layer leaves clove oil as the product.
The steps to be taken are:
1. Place ground cloves of garlic and water in a distilling flask
2. Distill the mixture (steam distillation)
3. Extract the clove oil into the dicholormethane and dry this with anhydrous NA2SO4
4. Remove the dichloromethane from the clove oil by distillation and finally weight the clove oil
In: Chemistry
[12] In an experiment on human behavior, a psychologist asks four men and four women to...
[12] In an experiment on human behavior, a psychologist asks four men and four women to enter a room and sit at a rectangular table. This table has three seats on each of the longer sides of the table, and one seat at each end of the table. The seats at the end of the table are considered to be the dominant seats. (A diagram may help you to visualize this).
a. If the people choose their seats randomly, determine the probability distribution for the random variable X, where X represents the number of women occupying the end seats. [4]
b. Determine E(X) and Var(X). [5]
c. In 15 independent repetitions of the experiment involving different people each time, calculate the probability that women occupy both end seats 2 or more times. [3]
In: Statistics and Probability