Questions
4. The following table presents the data on comparison of three methods of determining serum amylase...
4. The following table presents the data on comparison of three methods of determining serum amylase values in patients with pancreatitis. Test whether these data indicate a difference among the three methods.
|
Serum amylase values (enzyme units per 100 ml of serum) in patients with pancreatitis |
|||
|
Specimen |
Method of determination |
||
|
A |
B |
C |
|
|
1 |
4000 |
3210 |
6120 |
|
2 |
1600 |
1040 |
2410 |
|
3 |
1600 |
647 |
2210 |
|
4 |
1200 |
570 |
2060 |
|
5 |
840 |
445 |
1400 |
|
6 |
352 |
156 |
249 |
|
7 |
224 |
155 |
224 |
|
8 |
200 |
99 |
208 |
|
9 |
184 |
70 |
227 |
In: Statistics and Probability
Your company, DrugsRUs, has developed a generic angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor, Vasotec, as a pharmaceutical drug used primarily...
Your company, DrugsRUs, has developed a generic angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor, Vasotec, as a pharmaceutical drug used primarily for the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure. You are leading the regulatory strategy team and have been asked to describe the path to approval comparing introduction in the US versus Brasil.
Please discuss the following:
(1) Which agency or agencies will be responsible for approving/reviewing your Vastec drug: (a) before commercial introduction, and (b) after approval for commercialization/sale within the US., and
(2) Compare known issues your company will need to consider to market your generic drug is Brasil.
In: Biology
19) Core Concept: Information Flow- Explain how information from DNA results in the synthesis of a...
19) Core Concept: Information Flow- Explain how information from DNA results in the synthesis of a protein. Explain how information in the environment ultimately results in changes to gene expression.
20) Explain the steps in DNA recombinant technology (FROM GFP LAB). Include restriction enzymes, plasmids, heat shock, transformation and names of any enzyme that is needed in your answer.
21) Explain the purpose and/or what is happening at any step in the GFP lab protocols.
22) Predict how defects in the regulation of cell-cycle checkpoints would affect cells and explain how these defects relate to uncontrolled division in cancer and cancer progression.
In: Biology
The lacI gene regulates transcription of the structural genes by producing a repressor molecule that is...
The lacI gene regulates transcription of the structural genes by producing a repressor molecule that is allosteric, meaning that
|
it interacts irreversibly with a gene, causing both a conformational change in three-dimensional shape and a change in chemical activity of the enzyme |
||
|
it interacts reversibly with a gene, causing both a conformational change in three-dimensional shape and a change the protein it codes for |
||
|
it interacts irreversibly with another molecule, causing both a conformational change in three-dimensional shape and a change in chemical activity |
||
|
it can break down polysaccharides into small subunits. |
||
|
it interacts reversibly with another molecule, causing both a conformational change in three-dimensional shape and a change in chemical activity |
In: Biology
1. Which of the following are TRUE about sperm? Select one or more: a. Hyaluronidase is...
1. Which of the following are TRUE about sperm?
Select one or more:
a. Hyaluronidase is the enzyme involved in dissolving the protective coating around the unfertilized ovum.
b. The first sperm cell to reach the egg successfully fertilizes that cell.
c. Sperm cells have half the number of chromosomes as a spermatagoium and are about the same size.
d. Sperm cell capacitation, which occurs after ejaculation, is required for sperm cells to be active.
e. Mitochodria are located in the mid piece of the tail below the head.
f. The head of the sperm contains the DNA from the father.
g. The acrosome is located at the base of the sperm cell's tail.
In: Biology
16. Why does FADH2 provide energy for 1.5 ATP molecules in the ETC, whereas NADH provides...
16. Why does FADH2 provide energy for 1.5 ATP
molecules in the ETC, whereas NADH provides energy for 2.5 ATP
molecules? ( Show calculations. )
17. How does each of the following regulate the CAC:
a/ high levels of NADH
b/ high levels of ATP
c/ high levels of ADP
d/ low levels of NADH
18. Where is ATP synthase for oxidative phosphorylation located in
the cell?
19. Why do H+ leave the intermembrane space and return to the
matrix of the mitochondrion?
20. Why do the enzyme complexes that pump H+ extend across the
mitochondrial membrane from the matrix to the intermembrane
space?
In: Biology
The reaction A + B → C has a ∆G0’ of -20 kJ/mol at 25 0C....
The reaction A + B → C has a ∆G0’ of -20 kJ/mol at 25 0C. Starting under
Standard Conditions, one can predict that:
A. at equilibrium, the concentration of B will exceed the concentration of A.
B. at equilibrium, the concentration of C will be less than the concentration of A.
C. at equilibrium, the concentration of C will be much greater than the
concentration of A or B.
D. C will rapidly break down to A + B.
E. when A and B are mixed, the reaction will proceed rapidly toward formation
of C.
29. Estimate the value of Km for an enzyme-catalyzed reaction for which the
following data points were obtained.
[S] (M) V0 (mM/min)
2.5 x 10-6 28
4.0 x 10-6 40
1.0 x 10-5 70
2.0 x 10-5 95
4.0 x 10-5 112
1.0 x 10-4 128
2.0 x 10-3 139
1.0 x 10-2 140
A. 1.0 x 10-4
B. 1.0 x 10-3
C. 1.0 x 10-6
D. 1.0 x 10-5
E. 1.0 x 10-7
30. pH = pKa when:
[A-]/[HA] = 0
log ([A-]/[HA]) = 1
[A-] >> [HA]
[A-] = [HA]
log ([HA]/[A-]) = 1
31. In the conversion of A into D in the following biochemical pathway, enzymes
EA, EB, and EC have the Km values indicated under each enzyme. If all of the
substrates and products are present at a concentration of 10-4 M and the
enzymes have approximately the same Vmax which step will be rate limiting?
Rx1 Rx2 Rx3
A ↔ B ↔ C ↔ D
EA EB EC
Km = 10-2M 10-4M 10-4M
A. Rx 3
B. Rx 1
C. Rx 2
D. Rx’s 1 and 3
E. Rx’s 2 and 3
32. Consider the following Keq values with the appropriate ΔG0’?
Keq ΔG0’
A 1.0 1 28.53
B 10-5 2 -11.42
C 104 3 5.69
D 102 4 0
E 10-1 5 -22.84
A Keq of 102 would correspond to which of the following ΔG0’ values?
28.53
-11.42
5.69
0
-22.84
33. For an enzyme that follows simple Michaelis-Menten kinetics, what is the
value of Vmax if V0 is equal to 1 µmol minute-1 when [S] = 1/10 Km?
11.0 µmol minute-1
1.10 µmol minute-1
0.10 µmol minute-1
10.1 µmol minute-1
1.0 µmol minute-1
In: Chemistry
Purpose The clear understanding of energy transformations (Bioenergetics and Photosynthesis) by cells explains how cells...
Purpose
The clear understanding of energy transformations (Bioenergetics and Photosynthesis) by cells explains how cells can maintain their homeostasis in a continuously changing world. Completing this assignment will assist you in developing clarity of how cells function energetically on the planet and how some cells capture sunlight to build organic molecules. These principles of Bioenergetics and Photosynthesis will help clarify the Course Content Learning Outcomes number 2 (Understand the basic principles and ideas of chemistry and organic chemistry) and 4 (Able to explain the concept of a cell and describe the functions of its parts) for this course. This exercise will also clarify the Campus Wide Outcome of Critical Thinking (See page 3 (Critical Thinking) of the syllabus). The knowledge gained could assist students in other related science courses and courses in Psychology, Criminal Justice, and others.
Task
Armed with a textbook (Chapters 5 & 6), the Bioenergetics and Photosynthesis Power Point presentations, or other reliable sources answer the following questions about Bioenergetics and Photosynthesis. Be creative in how you approach and answer each question. Do not just copy and paste information from another source. Read the source and then write your answer in your own words so that it becomes your answer. Remember in science there are no “correct” answers but rather explanations of phenomena. This assignment will be due .....
Criteria
This assignment is worth .... total. The possible points for each question are in parenthesis after the question number. A complete answer to each question will involve being cognizant of the principles of Bioenergetics (The energy flow through a biological system.) and Photosynthesis (The harvesting of sunlight energy to build organic molecules.). Clear answers will have the involved cellular parts and molecules labeled clearly with descriptions and definitions that are clear, concise, and will contain enough detail that anyone reading your answer could potentially draw the same conclusions that you have by answering the questions.
- (5) Define the following terms as they relate to an enzyme: activation energy, active site,
conformation, denaturation, and coenzyme/cofactor binding site.
- (5) How are enzymes inhibited by competing and by non-competing molecules?
- (5) Draw a graph that would represent enzyme function at various temperatures and draw a
graph that would represent enzyme function at various pH levels.
- (5) Describe and give an example of the concept of energy coupling reactions in regards to cellular
ATP usage.
- (10) Describe the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis in five steps or less.
- (10) Describe the light independent reactions (Calvin cycle) of photosynthesis in five steps or less.
Divide the cycle into two halves: Molecule Building and Rearrangement before listing your steps to help focus your thoughts.
In: Biology
Q1 A research laboratory identified a gene X of medicinal value in a plant species. You...
Q1 A research laboratory identified a gene X of medicinal value in a plant species. You are given a small fragment of DNA containing gene X and the cloning vector pZoom. Maps of the 4 kb cloning vector pZoom and the 10 kb plant DNA fragment are shown in Figure 1 and 2, respectively. The PCR primer pairs (shown in Figure 1) F1/R1, F2/R2 and F3/R3 amplify fragments of 0.1, 0.6 and 0.8 kb, respectively. The antibiotic resistance gene A and gene B code for chloramphenicol and streptomycin resistance, respectively. The three restriction enzymes that cut this vector are BamHI, XbaI and HindIII represented on the map as enzymes I, II and III, respectively. You are given purified DNA of both the vector and the gene X containing DNA fragment at 0.2 µg/ul. Create a recombinant plasmid containing the complete gene X in the provided cloning vector pZoom. a. Design restriction digestion reactions using appropriate enzymes in such a way that you get a final concentration of 50 ng/µl for the digested vector and for the plant DNA (insert DNA) in the reaction. Your digestion should include all components in a 20 µL reaction. All enzymes are supplied with a concentration of 10 units/µL; you may use 1 µL of the enzyme in each reaction. Buffers for each enzyme are available as 10 times concentrated (10X) stocks. b. Generate three ligation reactions with 1:1, 2:1 and 3:1 molar ratios of the insert and the vector DNA. Your ligation should include all components in a 30 µL reaction. Keep the vector amount fixed at 100 ng per ligation reaction. You are provided with 10 x ligase buffer and DNA ligase (0.5 U/µL) to set up your ligations. c. Develop a strategy to select transformants and a quick method to screen recombinants; show your screening method using a figure. Predict the expected results with an explanation. d. Devise a restriction analysis method to confirm the desired recombinant; use a single most appropriate enzyme. Calculate the expected sizes of the restriction fragments from each, the vector and the desired recombinant. e. Devise a PCR strategy to confirm the desired recombinant. Calculate the expected sizes of the PCR fragments from the desired recombinant in a multiplex PCR including all three primer pairs. How will these sizes differ from the same multiplex PCR if the template is vector DNA instead of the recombinant plasmid?
In: Biology
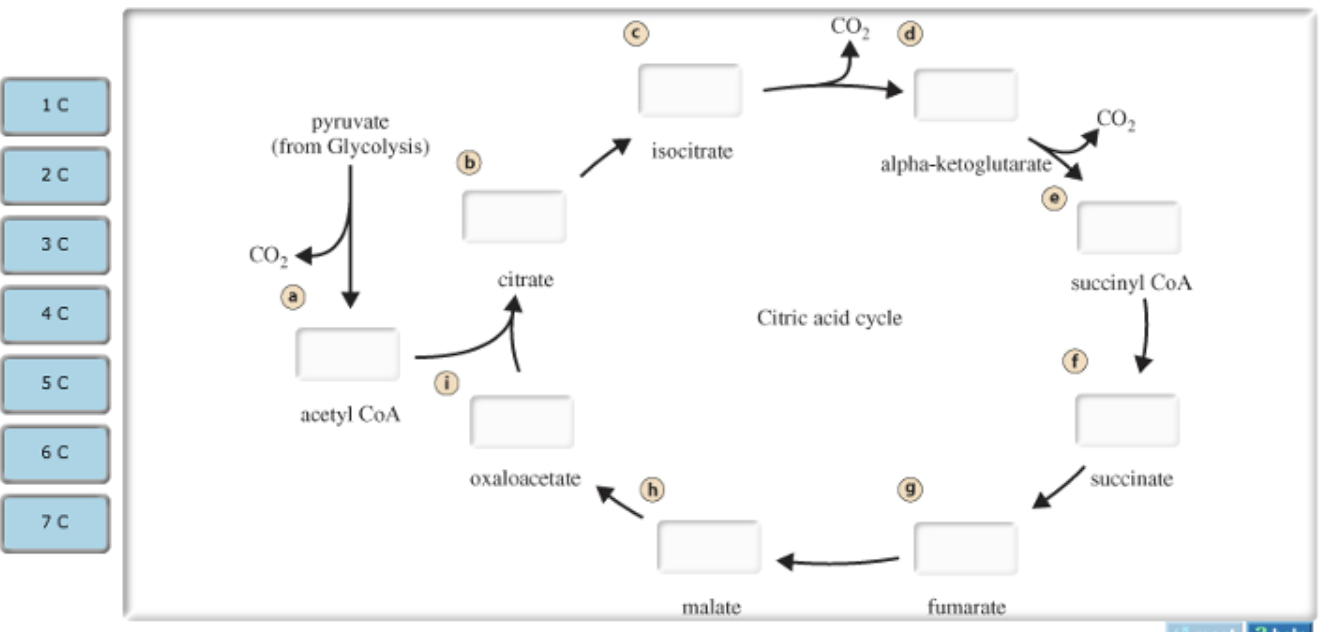
During acetyl CoA formation and the citric acid cycle, all of the carbon atoms that enter cellular respiration in the glucose molecule are released in the form of CO2.
Part A - Carbon atoms in acetyl CoA formation and the citric acid cycle
During acetyl CoA formation and the citric acid cycle, all of the carbon atoms that enter cellular respiration in the glucose molecule are released in the form of CO2. Use this diagram to track the carbon-containing compounds that play a role in these two stages.
Drag the labels from the left (which represent numbers of carbon atoms) onto the diagram to identify the number of carbon atoms in each intermediate in acetyl CoA formation and the citric acid cycle. Labels may be used more than once.
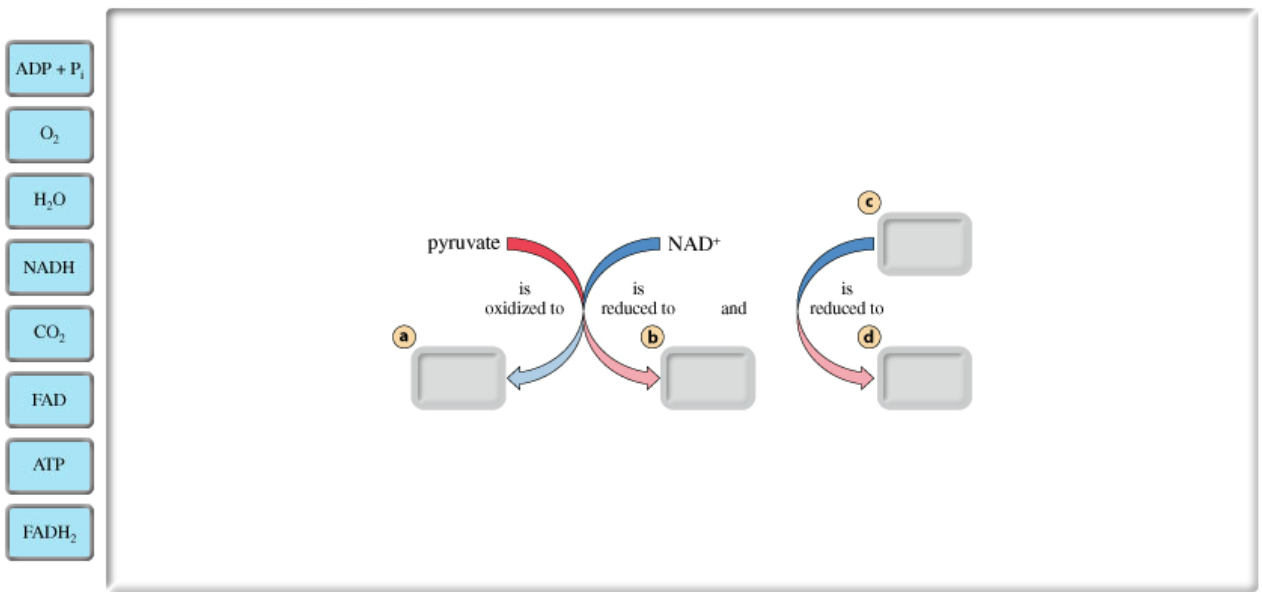
Part B - Net redox reaction in acetyl CoA formation and the citric acid cycle
In the sequential reactions of acetyl CoA formation and the citric acid cycle, pyruvate (the output from glycolysis) is completely oxidized, and the electrons produced from this oxidation are passed on to two types of electron acceptors.
Drag the labels on the left to show the net redox reaction in acetyl CoA formation and the citric acid cycle. Note that two types of electron carriers are involved.
Part C - Why is the citric acid cycle a cyclic pathway rather than a linear pathway?
In the oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, one carbon atom is released as \(\mathrm{CO}_{2}\). However, the oxidation of the remaining two carbon atoms-in acetate- -to \(\mathrm{CO}_{2}\), requires a complex, eight-step pathway-the citric acid cycle. Consider four possible explanations for why the last two carbons in acetate are converted to \(\mathrm{CO}_{2}\) in a complex cyclic pathway rather than through a simple, linear reaction.
- Use your knowledge of the first three stages of cellular respiration to determine which explanation is correct.
- More ATP is produced per \(\mathrm{CO}_{2}\), released in cyclic processes than in linear processes.
- It is easier to remove electrons and produce \(\mathrm{CO}_{2}\) from compounds with three or more carbon atoms than from a two-carbon compound such as acetyl CoA.
- Redox reactions that simultaneously produce \(\mathrm{CO}_{2}\) and NADH occur only in cyclic processes.
- Cyclic processes, such as the citric acid cycle, require a different mechanism of ATP synthesis than linear processes, such as glycolysis.
In: Biology