Questions
A survey of magazine subscribers showed that 45.9% rented a car during the past 12 months...
A survey of magazine subscribers showed that 45.9% rented a car during the past 12 months for business reasons, 53% rented a car during the past 12 months for personal reasons, and 29% rented a car during the past 12 months for both business and personal reasons.
(a)
What is the probability that a subscriber rented a car during the past 12 months for business or personal reasons?
(b)
What is the probability that a subscriber did not rent a car during the past 12 months for either business or personal reasons?
In: Statistics and Probability
Family Life Publications Inc.
Family Life Publications Inc. is considering two new magazine products. The estimated net cash flows from each product are as follows:
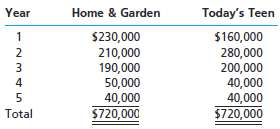
Each product requires an investment of $440,000. A rate of 15% has been selected for the net present value analysis.
Instructions
1. Compute the following for each project:
a. Cash payback period.
b. The net present value. Use the present value of $1 table appearing in this chapter.
2. Prepare a brief report advising management on the relative merits of each of the twoproducts.
In: Accounting
Step 1 Find examples of measures of central tendency and variability. Find an example of data...
Step 1
Find examples of measures of central tendency and variability.
Find an example of data presented in some print medium–newspaper, magazine, journal, etc.–and focus on the measures of central tendency and measures of variability.
Step 2
Write about your example.
Prepare your discussion posting by answering the following:
- Which measures or central tendency and variability were presented in the article?
- Were they presented correctly?
- Is there a clearer way the author could have presented the information?
- In what ways are the measures of central tendency and variability helpful to the reader?
In: Statistics and Probability
6) Unearned revenue is classified as a. an asset account. b. a revenue account. c. a...
6) Unearned revenue is classified as
a. an asset account.
b. a revenue account.
c. a contra-revenue account.
d. a liability account.
7) Which of the following would not result in unearned revenue?
a. Rent collected in advance from tenants
b. Services performed on account
c. Sale of season tickets to football games
d. Sale of two-year magazine subscriptions
8) If an adjusting entry is not made for an accrued expense,
a. expenses will be overstated.
b. liabilities will be understated.
c. net income will be understated.
d. owner’s equity will be understated.
In: Accounting
Find a current article related to international financial management from either a newspaper (i.e. The Globe...
Find a current article related to international financial management from either a newspaper (i.e. The Globe and Mail, National Post, etc. ) or business journal / magazine (i.e. Newsweek, Harvard Business Review, The Economist, etc.). Write a short paper on the article (about 5 pages) including the following (use these as headings):
1. Brief summary of the key points of the article,
2. Identify aspects of the article that relate to key concepts in the course and discuss the concepts briefly,
3. Discussion of implications for international financial management.
In: Operations Management
Choose any topic covered in our subject (except for poverty and inequality) and search online for...
Choose any topic covered in our subject (except for poverty and inequality) and search online for an interesting news article that relates to that topic. You are not required to submit a copy of the article with your answers.
Please state the following:
- Source of the article you chose (newspaper, magazine, etc.):
- Link:
- Topic covered in the subject that relates to the article:
- In no more than 200 words summarise the article and explain how it relates to the subject.
- In no more than 100 words explain why you think the article is interesting in the context of economic development.
In: Economics
5. Much of traditional advertising now incorporates some form of online promotion or information, even if...
5. Much of traditional advertising now incorporates some form of online promotion or information, even if it is as simple as including a website URL on a magazine, newspaper, or television advertisement. Each of the web addresses below leads to the online component of a traditional media ad campaign. Review each site and then answer these questions: What added value does the online component bring to the campaign? What other ways could the advertiser incorporate digital media in the campaign? Why would a consumer go the website, and why would he or she stay?
In: Operations Management
For this final discussion, I would like you to venture out beyond the information presented in...
For this final discussion, I would like you to venture out beyond the information presented in this class and find a news article or magazine article (something "current") that is related to a company software upgrade. Identify what software was updated and why, security concerns, etc. Explain how the story or example works in regards to the things we have focused on in this course. Given your newly acquired knowledge on these topics, what stands out to you from this story? Is there anything you feel could have been done better?
In: Computer Science
National polls are often conducted by asking the opinions of a few thousand adults nationwide and...
National polls are often conducted by asking the opinions of a few thousand adults nationwide and using them to infer the opinions of all adults in the nation. Explain who is in the sample and who is in the population for such polls. Please use a poll from a newspaper, TV, a magazine, or from the Internet (Chapter 8).
You may use the information in the textbook or cite a source.
Then answer your classmates' posts and comment on their description.
Please remember to use APA formatting if you use help from the textbook or a website. Try to use your own words!
In: Operations Management
. Wal-Mart’s Foreign Expansion Wal-Mart, the world’s largest retailer, has built its success on a strategy...
. Wal-Mart’s Foreign Expansion Wal-Mart, the world’s largest retailer, has built its success on a strategy of everyday low prices, and highly efficient operations, logistics, and information systems that keeps inventory to a minimum and ensures against both overstocking and understocking. The company employs some 2.1 million people, operates 4,200 stores in the United States and 3,600 in the rest of the world, and generates sales of almost $400 billion (as of fiscal 2008). Approximately $91 billion of these sales were generated in 15 nations outside of the United States. Facing a slowdown in growth in the United States, Wal-Mart began its international expansion in the early 1990s when it entered Mexico, teaming up in a joint venture with Cifra, Mexico’s largest retailer, to open a series of supercenters that sell both groceries and general merchandise. Initially the retailer hit some headwinds in Mexico. It quickly discovered that shopping habits were different. Most people preferred to buy fresh produce at local stores, particularly items like meat, tortillas and pan dulce which didn’t keep well overnight (many Mexicans lacked large refrigerators). Many consumers also lacked cars, and did not buy in large volumes as consumers in the United States did. WalMart adjusted its strategy to meet the local conditions, hiring local managers who understood Mexican culture, letting those managers control merchandising strategy, building smaller stores that people could walk to, and offering more fresh produce. At the same time, the company believed that it could gradually change the shopping culture in Mexico, educating consumers by showing them the benefits of its American merchandising culture. After all, Wal-Mart’s managers reasoned, people once shopped at small stores in the United States, but starting in the 1950s they increasingly gravitated towards large stores like WalMart. As it built up its distribution systems in Mexico, Wal-Mart was able to lower its own costs, and it passed these on to Mexican consumers in the form of lower prices. The customization, persistence, and low prices paid off. Mexicans started to change their shopping habits. Today Wal-Mart is Mexico’s largest retailer and the country is widely considered to be the company’s most successful foreign venture. Next Wal-Mart expanded into a number of developed nations, including Britain, Germany and South Korea. There its experiences have been less successful. In all three countries it found itself going head to head against well-established local rivals who had nicely matched their offerings to local shopping habits and consumer preferences. Moreover, consumers in all three countries seemed to have a preference for higher quality merchandise and were not as attracted to Wal-Mart’s discount strategy as consumers in the United States and Mexico. After years of losses, Wal-Mart pulled out of Germany and South Korea in 2006. At the same time, it continued to look for retailing opportunities elsewhere, particularly in developing nations where it lacked strong local competitors, where it could gradually alter the shopping culture to its advantage, and where its low price strategy was appealing. Recently, the centerpiece of its international expansion efforts has been China. Wal-Mart opened its first store in China in 1996, but initially expanded very slowly, and by 2006 had only 66 stores. What Wal-Mart discovered, however, was that the Chinese were bargain hunters, and open to the low price strategy and wide selection offered at Wal-Mart stores. Indeed, in terms of their shopping habits, the emerging Chinese middle class seemed more like Americans than Europeans. But to succeed in China, Wal-Mart also found it had to adapt its merchandising and operations strategy to mesh with Chinese culture. One of the things that Wal-Mart has learned is that Chinese consumers insist that food must be freshly harvested, or even killed in front of them. Wal-Mart initially offended Chinese consumers by trying to sell them dead fish, as well as meat packed in Styrofoam and cellophane. Shoppers turned their noses up at what they saw as old merchandise. So Wal-Mart began to display the meat uncovered, installed fish tanks into which shoppers could plunge fishing nets to pull out their evening meal, and began selling live turtles for turtle soup. Sales soared. Wal-Mart has also learned that in China, success requires it to embrace unions. Whereas in the United States Wal-Mart has vigorously resisted unionization, it came to the realization that in China unions don’t bargain for labor contracts. Instead, they are an arm of the state, providing funding for the Communist Party and (in the government’s view) securing social order. In mid- 2006 Wal-Mart broke with its long standing antagonism to unions and agreed to allow unions in its Chinese stores. Many believe this set the stage for Wal-Mart’s most recent move, the purchase in December 2006 of a 35 percent stake in the Trust-Mart chain, which has 101 hypermarkets in 34 cities across China. Now Wal-Mart has proclaimed that China lies at the center of its growth strategy. By early 2009 Wal-Mart had some 243 stores in the country, and despite the global economic slowdown, the company insists that it will continue to open new stores in China at a “double digit rate.”
Case Discussion Questions
1. Do you think Wal-Mart could translate its merchandising strategy wholesale to another country and succeed? If not, why not?
2. Why do you think Wal-Mart was successful in Mexico?
3. Why do you think Wal-Mart failed in South Korea and Germany? What are the differences between these countries and Mexico?
4. What must Wal-Mart do to succeed in China? Is it on track?
In: Economics