Questions
The statement of financial position of a company at year ended 31st December 2000 reflects the...
The statement of financial position of a company at
year ended 31st December 2000 reflects the following status:
Amount (Rs.)
Plant under installation 2000,000
Other assets 8000,000
10,000,000
Loans
Bank Loan 18% 2,000,000
Bank Loan 20% 2,500,000
Bank Loan 22% 1,500,000
6,000,000
Shareholder’s Equity 4,000,000
10,000,000
Bank loan of 20% was taken on April 1, 2000. Other
loans were brought forward from 1999.
Expenditures incurred on plant under installation:
April 01, 2000 1,000,000
June 01, 2000 700,000
September 01, 2000 300,000
2,000,000
Required: Calculate borrowing cost and total capitalized cost of asset at 2000.
In: Finance
Using the South University Online Library or the Internet, research database security and UML. Based on...
Using the South University Online Library or the Internet, research database security and UML.
Based on your research and readings for the week, respond to the following discussion topics.
- Often, systems have only one level of security when it comes to databases. Imagine that someone is trying to add a name (which should be composed only of letters) to a database. The user mistakenly hits a number, and the system rejects the entry. Such security can be implemented at the database management system (DBMS) or the application level. Where would you apply security? Justify your choice.
- What are some alternative practices or standards of utilizing UML for the visual representation of systems? When would you use UML over other standards? When are other standards preferable?
In: Computer Science
Match each description with the appropriate term. - A. B....
Match each description with the appropriate term.
|
|
In: Accounting
Suppose, Thompson Inc. purchased 70% of outstanding shares of Panna Corporation for $ 120,000 on January...
Suppose, Thompson Inc. purchased 70% of outstanding shares of Panna Corporation for $ 120,000 on January 1, 2018.
For non-wholly owned subsidiary, the consolidation of financial statements is a complex system. There will be two groups of shareholders – Controlling and non-controlling. There are many theories for the determination of non-controlling interest (NCI). One acceptable method of consolidating subsidiaries after January 1, 2011, is “Entity Theory”. Under this theory, the full fair value of the subsidiary is determined by combining the fair value of the controlling interest and the fair value of NCI.
Another theory for the determination of NCI value is “Parent Company Extension Theory” which is also acceptable method for the valuation of NCI after January 1,2011. Under IFRS, either entity theory or parent company extension theory can be used. It is also stated in IFRS that a gain on a bargain purchase can only be recognized by the acquirer. It means NCI must be measured at its share of fair value of the identifiable net assets.
In this situation, you are required to –
-
Explain the appropriate theory applicable for NCI valuation.(3)
In: Accounting
I need al functional and non functional requirements and design constraints for this system: Payroll Management...
I need al functional and non functional requirements and design constraints for this system: Payroll Management System As the head of Information Technology at Mena, Inc., you are tasked with building a new payroll management system to replace the existing system which is hopelessly out of date. Mena needs a new system to allow employees to record timecard information electronically and automatically generate paychecks based on the number of hours worked and total amount of sales (for commissioned employees). The new system will be state of the art and will have a Windows-based desktop interface to allow employees to enter and submit timecard information, enter purchase orders, change some employee preferences (such as payment method), and create various reports. The system will run on individual employee desktops throughout the entire company. For reasons of auditing, employees can only access and edit their own timecards and purchase orders. The system will retain information on all employees in the company (Mena currently has around 7,000 employees worldwide). The system must pay each employee the correct amount, on time, by the method that they specify (see possible payment methods described later). Mena, for cost reasons, does not want to replace one of their legacy databases, the Project Management Database, which contains all information regarding projects and charge numbers. The new system must work with the existing Project Management Database, which is a DB2 database running on an IBM mainframe. The Payroll System will access, but not update, information stored in the Project Management Database. Some employees (hourly employee) work by the hour, and they are paid an hourly rate. They must submit timecards that record the date and number of hours worked for a particular charge number. If someone works for more than 8 hours, Mena pays them 1.5 times their normal rate for those extra hours. Hourly workers are paid every Friday. Salaried employees are paid a flat salary. Even though they are paid a flat salary, they submit timecards that record the date and hours worked. This is done so the system can keep track of the hours worked against particular charge numbers. They are paid on the last working day of the month. Employees can login to the system using their unique IDs’ and passwords and they can only make changes to the timecard for the current pay period and before the timecard has been submitted. The system retrieves and displays the current timecard for the employee. If a timecard does not exist for the employee for the current pay period, the system creates a new one. The start and end dates of the timecard are set by the system and cannot be changed by the employee. If the timecards are submitted, the system makes the timecard read-only. Commissioned employees receive a commission based on their sales. They must be able to maintain purchase orders, which includes adding, changing, and deleting purchase orders. To add an order, Commissioned employees need to submit a purchase order that reflects the date, purchased products, and amount of the sale. It should also contain customer point of contact and customer billing address. The system is responsible for determining the commission rate for each employee, and it is one of 10%, 15%, 25%, or 35%. Also, the system will generate and assign a unique purchase order number to the purchase order, which will be provided to the Commissioned employees as a purchase reference. This unique number can be used later by the Commissioned employees to update their orders’ information, as well as, to delete it. One of the most requested features of the new system is employee reporting. Where employees will be able to request the system for the total hours worked, totals hours worked for a particular project, total pay received year-to-date, or remaining vacation time (vacation / sick leave), etc. In order to create these reports they need to indicate the type of the report, information related to each type, begin and end date of the report and the system will provide the report that satisfies the specified criteria. Employees may then request to print the report. Employees can choose their method of payment. The payment method controls how the Employee will be paid. They can have their paychecks mailed to a postal address of their choice, or they can request direct deposit and have their paycheck deposited into a specific bank account of their choosing. Also, They may choose to directly pick their paychecks up at the office. Mena Payroll Administrator can maintain employee information after he/she logs in to the system. He is responsible for adding new employees, deleting employees and changing all employees’ information such as name, mailing address, social security number, phone number, payment classification (hourly, salaried, commissioned), salary (for salaried and commissioned employees), hourly rate (for hourly employees), commission rate (for commissioned employees), tax deductions and other deductions. Once a new employee is added to the system, a unique ID number will be generated and assigned as an identification reference. Furthermore, the Payroll Administrator can run administrative reports. He can request to create either a “Total Hours Worked” or “Pay Year-to-Date” report. And in order to complete the request for those reports, the administrator must specify the following report criteria: the report type, employee name, begin and end dates for the report. The payroll application will run automatically every Friday and on the last working day of the month to generate the paychecks. It will pay the appropriate employees on those days. The system calculates the pay using entered timecards, purchase orders, employee information and all legal deductions. The system will be told what date the employees are to be paid, so it will generate payments for records from the last time the employee was paid to the specified date. The new system is being designed so that the payroll will always be generated automatically, and there will be no need for any manual intervention. Moreover, the system shall interface with existing bank systems via an electronic transaction in order to complete the deposit of the generated paychecks. The main system must be running most of the time. It is imperative that the system be up and running during the times the payroll is run (every Friday and the last working day of the month). Also, the system shall simultaneously support a large number of users against the central database at any given time. Additionally, the system should prevent employees from changing any timecards other than their own. Finally, only the Payroll Administrator is allowed to change any employee information with the exception of the payment delivery method. Payroll Management System Glossary The glossary contains the working definitions for the key concepts in the Mena Payroll Management System: 1. Bank System Any bank(s) to which direct deposit transactions are sent. 2. Employee A person who works for the company that owns and operates the payroll system (Mena, Inc.) 3. Payroll Administrator The person responsible for maintaining employees and employee information in the system. 4. Project Management Database The legacy database that contains all information regarding projects and charge numbers. 5. System Clock The internal system clock that keeps track of time. The internal clock will automatically run the payroll at the appropriate times. 6. Pay Period The amount of time over which an employee is paid. 7. Paycheck A record of how much an employee was paid during a specified Pay Period. 8. Payment Method How the employee is paid, either pick-up, mail, or direct deposit. 9. Timecard A record of hours worked by the employee during a specified pay period. 10. Purchase Order A record of a sale made by an employee. 11. Salaried Employee An employee that receives a salary. 12. Commissioned Employee An employee that receives a salary plus commissions. 13. Hourly Employee An employee that is paid by the hour.
In: Computer Science
Decide whether each pair of elements in the table below will form an ionic compound. If they will, write the empirical formula of the compound formed in the space provided.
Decide whether each pair of elements in the table below will form an ionic compound. If they will, write the empirical formula of the compound formed in the space provided.
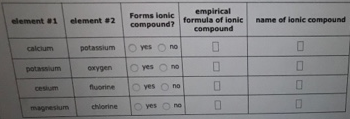
In: Chemistry
Explain the spillover benefits that are purported to flow from the athletic department to the university.
Explain the spillover benefits that are purported to flow from the athletic department to the university. What does empirical research indicate about these spillover benefits?
In: Economics
Which of the following types of articles would NOT be included in an embedded review of...
Which of the following types of articles would NOT be included in an embedded review of literature?
|
Theory articles. |
||
|
Methodological articles. |
||
|
Opinion articles. |
||
|
Empirical findings. |
In: Nursing
A hydrated nickel chloride compound was found to contain 24.69% Ni, 29.83% Cl, and 45.48% water....
A hydrated nickel chloride compound was found to contain 24.69% Ni, 29.83% Cl, and 45.48% water. Determine the empirical formula of this hydrated compound
In: Chemistry
A 17.65g of a hyrdocarbon undergoes complete combustion to yield 25.01g of CO2 and 10.59g of...
A 17.65g of a hyrdocarbon undergoes complete combustion to yield 25.01g of CO2 and 10.59g of H2O. Determine the mass of each element in the sample and the empirical formula
In: Chemistry