Questions
A) estimate the error in the values of the gaussian approximation of the binomial coefficients g(12,2s)...
A) estimate the error in the values of the gaussian approximation of the binomial coefficients g(12,2s) as 2s changes from 0 to its maximum value. (N=12 2s between states)
B) How will the error in the value g(N,0) calculated using the gausian approximation in A if you use N=20?
In: Math
Summarize clearly and completely how looking at the contour curves differs from looking at the cross...
In: Advanced Math
2. In a closed economy, how would each of the following events affect bond price and...
2. In a closed economy, how would each of the following events affect bond price and market interest rate? Use the figures of both bond market and market of loanable funds to illustrate the changes to the interest rates.
A. The expected rate of inflation decreases.
B. The federal government runs a budget deficit.
In: Economics
You now hold a position of power in our health care system. (You choose which position.)...
You now hold a position of power in our health care system. (You choose which position.) What three changes could you realistically attempt to make so that health care would be provided more ethically? Justify your decisions. Please write up to a page response.
In: Nursing
. You are working in Human Resources for a large corporation. The Chief Risk Officer (CRO)...
. You are working in Human Resources for a large corporation. The Chief Risk Officer (CRO) mentions to you that the cost of providing employee benefits continues to trend higher, and is seeking solutions. What are some possible changes that can be made to the employee benefits package that would help keep costs under control?
In: Operations Management
Find the following values, using the equations, and then work the problems using a financial calculator...
Find the following values, using the equations, and then work the problems using a financial calculator to check your answers. Disregard rounding differences. (Hint: If you are using a financial calculator, you can enter the known values and then press the appropriate key to find the unknown variable. Then, without clearing the TVM register, you can "override" the variable that changes by simply entering a new value for it and then pressing the key for the unknown variable to obtain the second answer. This procedure can be used in parts b and d, and in many other situations, to see how changes in input variables affect the output variable.) Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest cent.
-
An initial $700 compounded for 1 year at 4%.
$
-
An initial $700 compounded for 2 years at 4%.
$
-
The present value of $700 due in 1 year at a discount rate of 4%.
$
-
The present value of $700 due in 2 years at a discount rate of 4%.
$
In: Finance
The junction rule describes the conservation of which quantity?
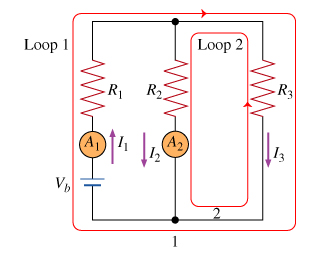
The junction rule describes the conservation of which quantity? Note that this rule applies only to circuits that are in a steady-state.
is it current, voltage or resistance
>Apply the junction rule to the junction labeled with the number 1 (at the bottom of the resistor of resistance R2).
Answer in terms of given quantities, together with the meter readings I1 and I2 and the current I3.
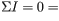
>Apply the loop rule to loop 2(the smaller loop on the right). Sum the voltage changes across each circuit element around this loop going in the direction of the arrow. Remember that the current meter is ideal.
Express the voltage drops in terms of Vb, I2 , I3 , the given resistances, and any other given quantities.
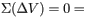
>Now apply the loop rule to loop 1 (the larger loop spanning the entire circuit). Sum the voltage changes across each circuit element around this loop going in the direction of the arrow.
Express the voltage drops in terms of Vb, I1 , I3 , the given resistances, and any other given quantities.
In: Physics
Find the following values, using the equations, and then work the problems using a financial calculator...
Find the following values, using the equations, and then work the problems using a financial calculator to check your answers. Disregard rounding differences. (Hint: If you are using a financial calculator, you can enter the known values and then press the appropriate key to find the unknown variable. Then, without clearing the TVM register, you can "override" the variable that changes by simply entering a new value for it and then pressing the key for the unknown variable to obtain the second answer. This procedure can be used in parts b and d, and in many other situations, to see how changes in input variables affect the output variable.) Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest cent.
a. An initial $300 compounded for 1 year at 6%. $
b. An initial $300 compounded for 2 years at 6%. $
c. The present value of $300 due in 1 year at a discount rate of 6%. $
d. The present value of $300 due in 2 years at a discount rate of 6%. $
In: Finance
Use both the TVM equations and a financial calculator to find the following values. (Hint: If...
Use both the TVM equations and a financial calculator to find the following values. (Hint: If you are using a financial calculator, you can enter the known values and then press the appropriate key to find the unknown variable. Then, without clearing the TVM register, you can "override" the variable that changes by simply entering a new value for it and then pressing the key for the unknown variable to obtain the second answer. This procedure can be used in parts b and d, and in many other situations, to see how changes in input variables affect the output variable.) Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answers to the nearest cent.
a. An initial $500 compounded for 10 years at 3%. $
b. An initial $500 compounded for 10 years at 6%. $
c. The present value of $500 due in 10 years at a 3% discount rate. $
d. The present value of $500 due in 10 years at a 6% discount rate. $
In: Finance
Which of the following statements about evaluating a single project where costs occur before benefits is...
Which of the following statements about evaluating a single project where costs occur before benefits is FALSE?
Group of answer choices
A. In an NPV profile that shows how NPV changes when cost of capital changes, NPV equals zero when the project discount rate equals IRR.
B. In general, the difference between the cost of capital and the internal rate of return (IRR) is the maximum amount of estimation error in the cost of capital estimate that can exist without altering the original decision.
C. If you are unsure of your cost of capital estimate, it is important to determine how sensitive your analysis is to errors in this estimate.
D. The internal rate of return (IRR) can provide information on how sensitive your analysis is to errors in the estimate of your cost of capital.
E. If the cost of capital estimate is more than the internal rate of return (IRR), the net present value (NPV) will be positive.
In: Finance