Questions
Multiple Choice 1 Data differ from information in which way? a. Data are facts about a...
Multiple Choice 1
Data differ from information in which way?
a. Data are facts about a sale
b. Information is data organized to provide meaning
c. Data are meaningful bits of information
d. There is no difference
Multiple Choice 2
Which of the following is not a characteristic that makes information useful?
a. It is reliable
b. It is timely
c. It is inexpensive
d. It is relevant
Multiple Choice 3
What information needs are generally associated with the acquire inventory business process?
a. Market Analysis
b. Vendor Performance
c. Inventory status reports
d. All of the above
Multiple Choice 4
Which transaction cycle includes interactions between an organization and its suppliers?
a. Revenue cycle
b. Expenditure cycle
c. Human resources/payroll cycle
d. General ledger and reporting system
Multiple Choice 5
In which cycle does a company ship goods to customers?
a. Production cycle
b. Financing cycle
c. Revenue cycle
d. Expenditure cycle
Multiple Choice 6
Which of the following is a function of an AIS?
a. Reducing the need to identify a strategy and strategic position.
b. Transforming data into useful information.
c. Allocating organizational resources.
d. Automating all decision making.
Multiple Choice 7
An AIS provides value by:
a. improving products or services through information that increases quality and reduces costs
b. providing timely and reliable information to decision makers
c. creating new products
d. both A and B
Multiple Choice 8
The value chain concept is composed of the following two types of activities:
Primary and secondary
Primary and support
Support and value
Technology and support
Multiple Choice 9
Which of the following is a primary activity in the value chain?
a. Purchasing
b. Accounting
c. Post-sales service
d. Human resource management
Multiple Choice 10
Which of the following is a support activity in the value chain?
a. Purchasing
b. Manufacturing
c. Post-sales service
d. Receiving materials
In: Accounting
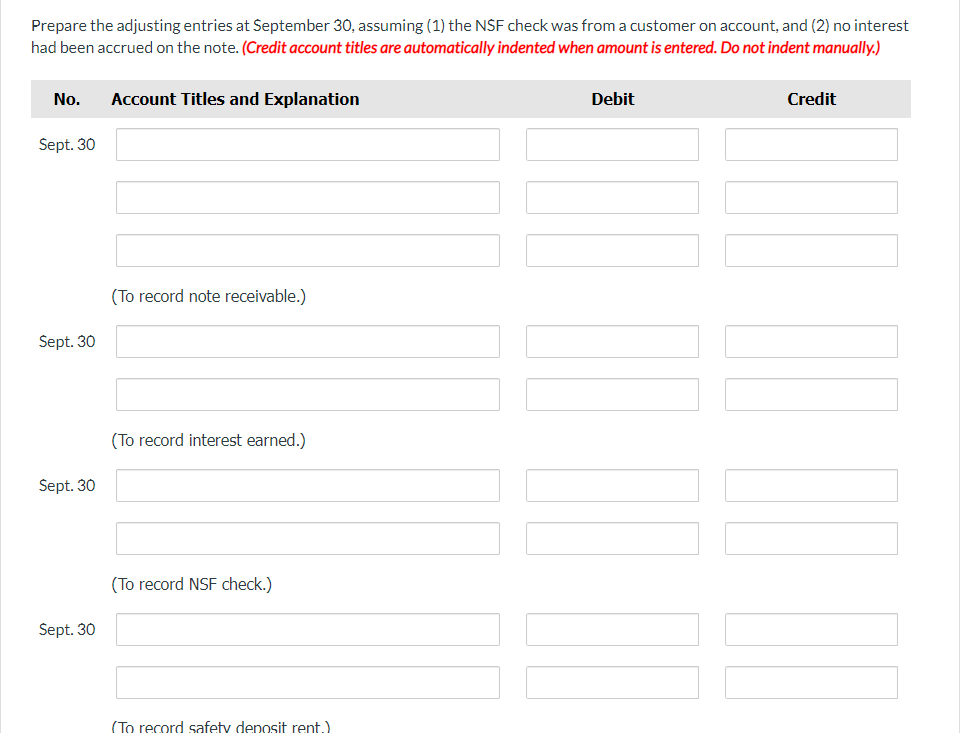
Prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement from the information provided and prepare adjusting Journal Entries.
Prepare a Bank Reconciliation Statement from the information provided and prepare adjusting Journal Entries.
The information below relates to the Cash account in the ledger of Bramble Company.
| Balance September 1—$17,010; | Cash deposited—$64,500. | |
| Balance September 30—$17,664; | Checks written—$63,846. |
The September bank statement shows a balance of $16,682 on September 30 and the following memoranda.
Credits | Debits | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Collection of $1,621 note plus interest $39 | $1,660 | NSF check: Richard Nance | $555 | |||
Interest earned on checking account | $54 | Safety deposit box rent | $74 |
At September 30, deposits in transit were $4,580, and outstanding checks totaled $2,513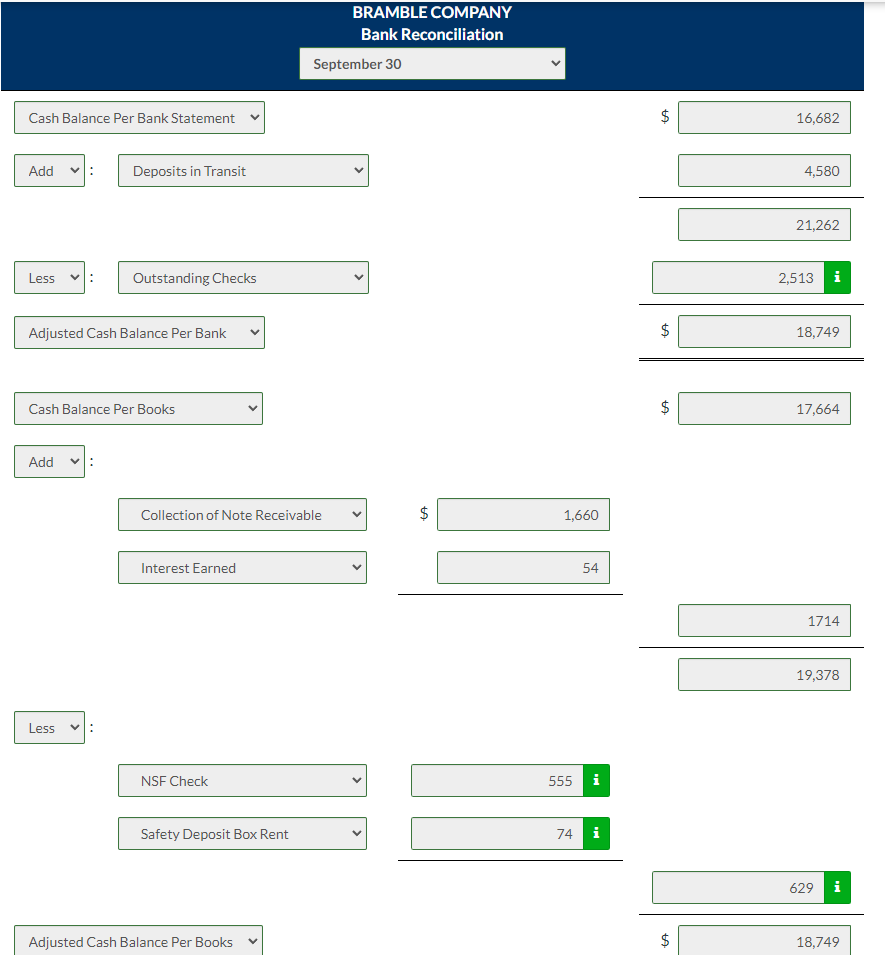
In: Accounting
At the end of the fiscal year ending 31st December 2018, MCS & Co reported common...
At the end of the fiscal year ending 31st December 2018, MCS & Co reported common equity of 649 million on its statement of financial position with 490 million invested in financial assets (in the form of cash equivalent and short term investments) and no financing debt. For the fiscal year ending 31st December 2019, the company reported 74 million in comprehensive income of which 11 million was after tax earnings on the financial assets. This month MCS & Co is distributing 340 million of financial assets to the shareholders in the form of special dividends.Holding all else constant, what would be MCS & Co ROCE after the payout of the 340 million as special dividends.
In: Finance
For its three investment centers, Gerrard Company accumulates the following data: I II III Sales $1,920,000...
For its three investment centers, Gerrard Company accumulates the following data:
I II III
Sales $1,920,000 $4,013,000 $4,033,000
Controllable margin 833,510 2,486,510 4,083,400
Average operating assets 4,903,000 8,021,000 12,010,000
The centers expect the following changes in the next year: (I) increase sales 14%; (II) decrease controllable fixed costs $404,000; (III) decrease average operating assets $534,000.
Compute the expected return on investment (ROI) for each center. Assume center has a contribution margin percentage of 74%. (Round ROI to 1 decimal place, e.g. 1.5.)
| I: % | II: % | III: % |
In: Accounting
For each of the following, evaluate if it is a good argument. Provide reasons for why...
For each of the following, evaluate if it is a good argument. Provide reasons for why or why not.
16. Tax. Jane is doing an income tax return. There are two different methods of determining some revenues. If method A is used her taxable income will be $50,000. If method B is used, her taxable income will be $56,000. Jane thinks that she better chooses method A.
17. Taxi driver. King is a taxi driver working for a yellow cab company in a developing country. Mostly, the drivers take cash and receipts are not issued. Only King knows how much revenue is generated from fares. King’s wage is 30% of the reported fare revenue. Whatever revenue he reports, he has to turn in that amount to the company first. To maximize his wages, King believes that he wants to over-report the fare revenue to the company.
18. Saved money? We were looking for a three bedroom house. We were three people. Our budget was $ $240,000 ($80,000 per bedroom). We actually paid $220,000 for a three bedroom house. Soon after, one of us left for another state, and one bedroom is empty. We saved $20,000, and it is good news for us.
In: Economics
Making Decisions Wexly is a large publicly owned corporation which you are the president. When making...
Making Decisions
Wexly is a large publicly owned corporation which you are the president. When making decisions, do you make them to maximize stockholders’ wealth or for your personal gains? What actions could stockholders take to make sure the interest of both parties is served? What can influence management’s actions?
In: Finance
The general ledger of Pop's Fireworks includes the following account balances in 2021: Accounts Debit Credit...
The general ledger of Pop's Fireworks includes the following account balances in 2021:
| Accounts | Debit | Credit | |||||
| Cash | $ | 24,600 | |||||
| Accounts Receivable | 50,000 | ||||||
| Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts | $ | 5,600 | |||||
| Supplies | 11,800 | ||||||
| Notes Receivable (8%, due in 2 years) | 44,000 | ||||||
| Land | 102,000 | ||||||
| Accounts Payable | 15,700 | ||||||
| Common Stock | 174,000 | ||||||
| Retained Earnings | 31,600 | ||||||
| Service Revenue | 128,200 | ||||||
| Salaries Expense | 72,600 | ||||||
| Utilities Expense | 29,300 | ||||||
| Supplies Expense | 20,800 | ||||||
| Totals | $ | 355,100 | $ | 355,100 | |||
In addition, the following transactions occurred during 2021 and are not yet reflected in the account balances above:
| June | 3 | Provide additional services on account for $24,000. All services on account include terms 2/10, n/30. | ||
| June | 8 | Receive cash from customers within 10 days of the services being provided on account. The customers were originally charged $13,500. | ||
| November | 15 | Write off customer accounts of $3,200 as uncollectible. |
1. Record each of the transactions listed above.
2. Record the following adjusting entries on December 31. (If no entry is required for a particular transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.)
- Estimate that 10% of the balance of accounts receivable (after transactions in requirement 1) will not be collected.
- Accrue interest on the note receivable of $44,000, which was accepted on October 1, 2021. Interest is due each September 30.
3. Prepare an adjusted trial balance as of December 31, 2021.
4. Prepare an income statement for the period ended December 31, 2021. (Amounts to be deducted should be indicated with a minus sign.)
5. Prepare a classified balance sheet as of December 31, 2021.
6. Record closing entries. (If no entry is required for a particular transaction/event, select "No Journal Entry Required" in the first account field.)
-Record the closure of revenue accounts.
-Record the closure of expense accounts.
7. Analyze the following information:
-
By how much does the year-end estimate of future uncollectible accounts reduce net income in 2021?
-
What is the ending balance of Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts?
-
What amount of cash is expected to be collected from accounts receivable?
| a. | Bad Debt Expense | |
| b. | Ending Balance of Allowance for Uncollectible Accounts | |
| c. | Amount Expected to be collected |
In: Accounting
Case 6-29 Variable and Absorption Costing Unit Product Costs and Income Statements [LO6-1, LO6-2] [The following...
Case 6-29 Variable and Absorption Costing Unit Product Costs and Income Statements [LO6-1, LO6-2]
[The following information applies to the questions displayed below.]
O’Brien Company manufactures and sells one product. The following information pertains to each of the company’s first three years of operations:
| Variable costs per unit: | ||
| Manufacturing: | ||
| Direct materials | $ | 27 |
| Direct labor | $ | 15 |
| Variable manufacturing overhead | $ | 4 |
| Variable selling and administrative | $ | 3 |
| Fixed costs per year: | ||
| Fixed manufacturing overhead | $ | 580,000 |
| Fixed selling and administrative expenses | $ | 110,000 |
During its first year of operations, O’Brien produced 91,000 units and sold 79,000 units. During its second year of operations, it produced 84,000 units and sold 91,000 units. In its third year, O’Brien produced 83,000 units and sold 78,000 units. The selling price of the company’s product is $78 per unit.
Case 6-29 Part-3
3. Assume the company uses absorption costing and a FIFO inventory flow assumption (FIFO means first-in first-out. In other words, it assumes that the oldest units in inventory are sold first):
a. Compute the unit product cost for Year 1, Year 2, and Year 3.
b. Prepare an income statement for Year 1, Year 2, and Year 3.
In: Accounting
1. Stratford Company reported the following information related to its operations for the year ended December...
1.
Stratford Company reported the following information related to its operations for the year ended
December 31, 2019. The owner, Ms. Keith, has asked you, Senior Accountant, to perform
some calculations in an effort to determine which inventory valuation method to select for
financial reporting purposes.
|
Date |
# of Units |
Unit Cost |
|
|
February 17 |
Beginning inventory |
145 |
$25 |
|
May 23 |
Purchase |
193 |
$28 |
|
August 19 |
Purchase |
127 |
$32 |
|
December 31 |
Purchase |
74 |
$35 |
The company sold 415 units throughout the year at a price of $60 each.
a) Is this company operating in an inflationary or deflationary environment? Explain how you know.
- Compute the dollar value of ending inventory under the following alternative methods:
- FIFO
- Weighted-average cost
- Compute the dollar value of cost of goods sold under the following alternative methods:
- FIFO
- Weighted-average cost
- If Stratford Company sold each unit for $58, calculate the gross profit under the following assumptions:
- FIFO
- Weighted-average
In: Accounting
Problem: An electric company has committed to building a solar power plant. An engineer tasked with...
Problem:
An electric company has committed to building a solar power plant. An engineer tasked with the company has been tasked with evaluating three solar power generation technologies. The power company uses an interest rate of 10% and a 20-year planning horizon for choosing the project that best fits its budgetary and financial goals.
Design 1: Flat Solar Panels: A field of flat solar panels angled to best catch the incident solar radiation wis expected to yield a power of 2.6 MW and will cost $87 million initially with first year operating costs of $2 million, growing 250,000 annually. It will produce electricity worth $6.9 million the first year; this revenue stream is expected to increase at a simple interest rate of 12%, every year from there on (that is, 112% of 6.9 Mil in year 2, 124% of 6.9 Mil in Year 3 etc.) .
Design 2: Mechanized solar panels: A field of mechanized solar panels with motors that allow panel frame motion so that the panel themselves will be normal to incident radiation anytime of the day. This design is expected to yield a power of 3.1 MW and will cost $101 million initially with first year operating costs of $2.3 million, growing 300,000 annually. It will produce electricity worth $8.8 million the first year; this revenue stream is expected to increase at a simple interest rate of 8%, every year from there on (that is, 112% of 8.8 Mil in year 2, 124% of 8.8 Mil in Year 3 etc.) .
Design 3: Solar Collector Field: This design uses a series of Fresnel lenses and concave mirrors to concentrate solar radiation onto a boiler mounted on a tower. The boiler then produces steam, which then is used to generate electricity. This system is expected to yield a power of 3.3 MW and will cost $91 million initially with first year operating costs of $3 million, growing 350,000 annually. It will produce electricity worth $9.7 million the first year; this revenue stream is expected to increase at a simple interest rate of 8%, every year from there on (that is, 112% of 9.7 Mil in year 2, 124% of 9.7 Mil in Year 3 etc.).
What would your suggestion be to the Engineer in regard to which Design to choose based on economic considerations only?
You must show the Economic logic equations (F/P, P/F, etc.) and their solutions
In: Economics