Questions
Compact fluorescent bulbs are much more efficient at producing light than are ordinary incandescent bulbs. They...
Compact fluorescent bulbs are much more efficient at producing light than are ordinary incandescent bulbs. They initially cost much more, but last far longer and use much less electricity. According to one study of these bulbs, a compact bulb that produces as much light as a 100 Wincandescent bulb uses only 23.0 W of power. The compact bulb lasts 1.00×104 hours, on the average, and costs $ 12.0 , whereas the incandescent bulb costs only 76.0 ¢, but lasts just 750 hours. The study assumed that electricity cost 9.00 ¢ per kWh and that the bulbs were on for 4.0 h per day.
(A) What is the total cost (including the price of the bulbs) to run incandescent bulbs for 3.0 years?
(B) What is the total cost (including the price of the bulbs) to run compact fluorescent bulbs for 3.0 years?
(C) How much do you save over 3.0 years if you use a compact fluorescent bulb instead of an incandescent bulb?
(D) What is the resistance of a "100 W" fluorescent bulb? (Remember, it actually uses only 23 W of power and operates across 120 V.)
In: Physics
A firm faces the following costs: total cost of capital = $2,000; price paid for labor...
A firm faces the following costs: total cost of capital = $2,000; price paid for labor = $12 per labor unit; and price paid for raw materials = $4 per raw-material unit.
Instructions: In parts a and b, round your answers to 2 decimal places. In part c, enter your answer as a whole number.
a. Suppose the firm can produce 6,000 units of output this year by combining its fixed capital with 100 units of labor and 450 units of raw materials. What are the total cost and average total cost of producing the 6,000 units of output?
TC=
ATC=
b. Now assume the firm improves its production process so that it can produce 7,000 units of output this year by combining its fixed capital with 100 units of labor and 450 units of raw materials. What are the total cost and average total cost of producing the 7,000 units of output?
TC=
ATC=
c. If units of output can always be sold for $1 each, then by how much does the firm’s profit increase after it improves its production process?
In: Economics
A charity organization hosts a raffle drawing at a fund raising event. The organization sells 2500...
A charity organization hosts a raffle drawing at a fund raising event. The organization sells 2500 tickets at a price of $8 each. Winning tickets are randomly selected, with 30 prizes of $100, 10 prizes of $500, and 1 grand prize of $8000. Suppose you buy one ticket. Let the random variable X represent your net gain from playing the game once (remember that the net gain should include the cost of the ticket). Use the table below to help you construct a probability distribution for all of the possible values of X and their probabilities. Find the mean/expected value of X. (Round to two decimal places.) In complete sentences, describe the interpretation of what your value from #2 represents in the context of the raffle. If you were to play in such a raffle 100 times, what is the expected net gain? Would you choose to buy a ticket for the raffle? (Your response should be a short paragraph, written in complete sentences, to explain why or why not.) What ticket price would make it a fair game, so that, on average, neither the players nor the organizers of the raffle win or lose money? (Round to two decimal places.)
In: Math
1. Ocular Solutions recently (at the beginning of year 1) forecasted first year sales of $9.4...
1. Ocular Solutions recently (at the beginning of year 1) forecasted first year sales of $9.4 million, operating costs other than depreciation of $5.6 million, and depreciation of $0.6 million. The company has no amortization charges, it has $4.2 million of outstanding bonds that carry a 6.5% interest rate, and its income tax rate is 28%. In order to sustain its operations and thus generate sales and cash flows in the future, the firm is required to make $1.3 million of capital expenditures on new fixed assets and to invest $0.3 million in net working capital.
a) Calculate the FCF of the firm in the first year. [5 Marks]
b) Assuming that the firm’s FCF will grow at a rate of 3% forever after Year 1, and also that its WACC is 20.0%, estimate the market value of the firm and its debt ratio (Debt/Firm Value) at the beginning of year 1. [5 Marks]
c) If the company keeps the debt level unchanged in the future, estimate its debt ratio at the beginning of year 2, and beginning of year 3. [5 Marks] d) Discuss the potential problem when using the WACC method to answer parts b) and c) above.
2. American Hardware (AH), a national hardware chain, is considering purchasing a smaller chain, Eastern Hardware (EH). American Hardware's analysts project that the merger will result in incremental free cash flows and interest tax savings. In the first two years, the incremental FCF is $3 million each year and the value increases to $3.5 million each year after the period. The tax savings are $0.5 million annually starting from the first year. They have determined that the appropriate discount rate for valuing EH (for both FCF and interest tax savings) is 17 percent. EH has 7 million shares outstanding and AH has 56 million shares outstanding. EH's current share price is $14.25 and AH’s current share price is $28.25. a). What is the maximum price per share that AH should offer (under the condition that all of the proposed synergy value is distributed to the EH shareholders)? [6 marks] b). If the proposed synergy value is equally distributed between AH shareholders and EH shareholders (50% to all AH shareholders and 50% to all EH shareholders), what is the price per share that AH should offer? [7 marks] c). If AH has successfully purchased all of EH shares at the price of $18, what should AH share price be after the purchasing (assuming investors know the information precisely as described above)?
a). What is the maximum price per share that AH should offer (under the condition that all of the proposed synergy value is distributed to the EH shareholders)? [6 marks] b). If the proposed synergy value is equally distributed between AH shareholders and EH shareholders (50% to all AH shareholders and 50% to all EH shareholders), what is the price per share that AH should offer? [7 marks] c). If AH has successfully purchased all of EH shares at the price of $18, what should AH share price be after the purchasing (assuming investors know the information precisely as described above)?
b). If the proposed synergy value is equally distributed between AH shareholders and EH shareholders (50% to all AH shareholders and 50% to all EH shareholders), what is the price per share that AH should offer?
c). If AH has successfully purchased all of EH shares at the price of $18, what should AH share price be after the purchasing (assuming investors know the information precisely as described above)?
In: Finance
answer the question Spud Co. is a dealer in potatoes. Chip Co. makes potato chips. On...
In: Finance
Draw a hypothetical demand and supply curves for egg cups in Canada, and then graph and...
Draw a hypothetical demand and supply curves for egg cups in Canada, and then graph and explain the following events and how they affect the equilibrium price and quantity of egg cups in Canada.
- A successful advertising campaign by egg cup producers.
- Technological improvements in the production of egg cups.
- An increase in the price of eggs a compliment in consumption.
- An increase in the price of bird feed the main input in egg production.
- An increase in the demand for waffles a substitute in consumption of eggs.
- Unemployment (show all work)
Suppose that country a population of 120 made up of a labour force of 100 and 20 children under the age of 15,
- What is the participation rate.
Eight members of the labour force are unemployed
- What is the unemployment rate?
Of the eight unemployed 2 worked in a factory that produced pies this factor has closed down and expected to open up after the pandemic.
- Describe what type of unemployment this is and why.
One of the eight is a sky instructor and has been laid off for the summer
- Describe what type of unemployment this is and why.
One of the unemployed cannot find a job and gives up looking
- What is the new unemployment rate
- Inflation (show all work)
Name the two measurements of inflation discussed in class
1)
2)
Using 2012 as the base year (=100) calculate the inflation rate for 2013
|
Year |
Slices of Pizza |
Price per Slice |
Cans of Pepsi |
Price per Can |
|
2012 |
40 |
10 |
10 |
20 |
|
2013 |
60 |
12 |
20 |
24 |
What does currency depreciation mean?
Who is the only legal issuer of bank notes and coins in Canada?
A responsible government believes that the inflation rate is out of control, what fiscal policies could they enact?
4) Economic Growth
|
2017 |
2018 |
|||
|
Product |
Quantity |
Price |
Quantity |
Price |
|
Backpacks |
100 |
$10 |
120 |
$12 |
|
Books |
50 |
$15 |
40 |
$20 |
Using 2017 as a base year, calculate;
1) The GDP deflator
2) Nominal Economic growth
3) Real economic growth
4) Give reasons why Real GDP per capita may overstate the well-being of a countries inhabitants?
5) MATCHING
Match the terms on the right to the ones on the left by placing the appropriate CAPITAL letter on the space provided. All the phrases are designed to fit; some may fit more than once. In any case, provide only one answer for each term. Illegible answers will be marked as wrong.
- _____ easy money policy A. increases competition
- _____ M2+ B. imports become cheaper
- _____ C $ depreciates C. expansionary fiscal policy
- _____ reduction in Gov. spending D. reduces competition
- _____ non-tariff barrier E. used to reduce inflationary pressures
- _____ C $ appreciates F. includes notice deposits of banks
- _____ free trade G. tight fiscal policy
- _____ tax reduction H. Exports become cheaper
- _____ M 1 I. interest rates fall
- ____ tight money policy J. currency plus demand deposits in banks
In: Economics
Let X denote the distance (m) that an animal moves from its birth site to the...
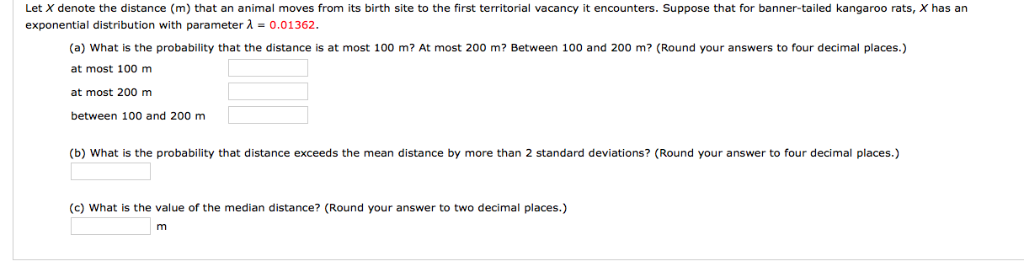
Let X denote the distance (m) that an animal moves from its birth site to the first territorial vacancy it encounters. Suppose that for banner-tailed kangaroo rats, X has an exponential distribution with parameter λ = 0.01362.
(a) What is the probability that the distance is at most 100 m?
(b) What is the probability that distance exceeds the mean distance by more than 2 standard deviations?
(c) What is the value of the median distance? (Round your answer to two decimal places.)
In: Math
Alice wants to sell her Pokemon card collection on eBay. She decides to accept the first...
Alice wants to sell her Pokemon card collection on eBay. She decides to accept the first bid that exceeds 100$. Suppose that each bid that she receives is chosen uniformly at random between 0$ and 110$ (the bids are continuous, i.e., real numbers in that interval). Let X be the number of bids Alice receives (once she accepts a bid, the auction is over and she does not receive any more bids).
(a)Is X discrete, continuous, or neither?
(b)Find the expectation of X.
In: Statistics and Probability
Please give me the journal entry for the first interest payment on each of the following...
Please give me the journal entry for the first interest payment on each of the following bond issues:
1. We issued bonds at 102% with a par of $1,000 a life of 20 years with an interest rate of 10%
2. We issued bonds at 98% with a par of $1,000 a life of 5 years with an interest rate of 9%
3. We issued bonds at 100% with a par of $1,000 a life of 2 years with an interest rate of 8%
Don't forget to amortize the premium or discount.
In: Accounting
Sweet Company’s outstanding stock consists of 1,300 shares of cumulative 5% preferred stock with a $100...
Sweet Company’s outstanding stock consists of 1,300 shares of
cumulative 5% preferred stock with a $100 par value and 10,300
shares of common stock with a $10 par value. During the first three
years of operation, the corporation declared and paid the following
total cash dividends.
| Dividends Declared & Paid | ||
| Year 1 | $ | 2,300 |
| Year 2 | $ | 6,300 |
| Year 3 | $ | 33,500 |
The total amount of dividends paid to preferred and common
shareholders over the three-year period is:
In: Accounting