Questions
The ABC Company is one of the largest producers of power tools in the United States....
The ABC Company is one of the largest producers of power tools in the United States. The company is preparing to replace its current product line with the next generation of products: specifically, three exciting new power tools with the latest state-of-the-art features. Because of the limited amount of capital available, management needs to make some difficult choices about how much to invest in each of these products. Another concern is the effect of these decisions on the company’s ability to maintain a relatively stable employment level. In addressing these decisions, management wants primary consideration given to three factors: total profit, stability in the workforce, and the level of capital investment needed to launch these products.
Goal 1: Achieve a total profit (NPV) of at least $250 million.
Goal 2: Maintain the current employment level of 8,000 employees. Goal 3: Hold the capital investment down to no more than $110 million.
All goals are important, but by small margin their order of importance is: Priority 1: Goal 1,
Priority 2: Goal 3,
Priority 3: Part of Goal 2 (avoid increasing the employment level), Priority 4: Part of Goal 2 (avoid decreasing the employment level)
The company estimated contributions per unit of each product along with all the necessary information as follows:
|
Factor |
P1 |
P2 |
P3 |
Goal |
|
Total profit ($mil) |
12 |
9 |
15 |
≥ 250 |
|
Employee level (00s) |
5 |
3 |
4 |
= 80 |
|
Capital investment ($mil) |
5 |
7 |
8 |
≤ 110 |
|
Goal |
Factor |
Penalty Weight for Missing Goal |
|
1 |
Total profit |
50 (per $1 mil under the goal) |
|
2 |
Employment level |
20 (per 100 employees under the goal 30 (per 100 employees over the goal) |
|
3 |
Capital investment |
40 (per $1 mil over the goal) |
- Formulate the above problem into Goal Programming (GP).
- Find the optimal solution (Attach Excel file).
In: Operations Management
The ABC Company is one of the largest producers of power tools in the United States.
The ABC Company is one of the largest producers of power tools in the United States. The company is preparing to replace its current product line with the next generation of products: specifically, three exciting new power tools with the latest state-of-the-art features. Because of the limited amount of capital available, management needs to make some difficult choices about how much to invest in each of these products. Another concern is the effect of these decisions on the company's ability to maintain a relatively stable employment level. In addressing these decisions, management wants primary consideration given to three factors: total profit, stability in the workforce, and the level of capital investment needed to launch these products.
Goal 1: Achieve a total profit (NPV) of at least $250 million.
Goal 2: Hold the capital investment down to no more than $110 million.
Goal 3: Maintain the current employment level of 8,000 employees.
All goals are important, but by small margin their order of importance is:
Priority 1: Goal 1
Priority 2: Goal 2
Priority 3: Part of Goal 3 (avoid decreasing the employment level)
Priority 4: Part of Goal 3 (avoid increasing the employment level)
The company estimated contributions per unit of each product to the goals along with all the nscessary information as follows:
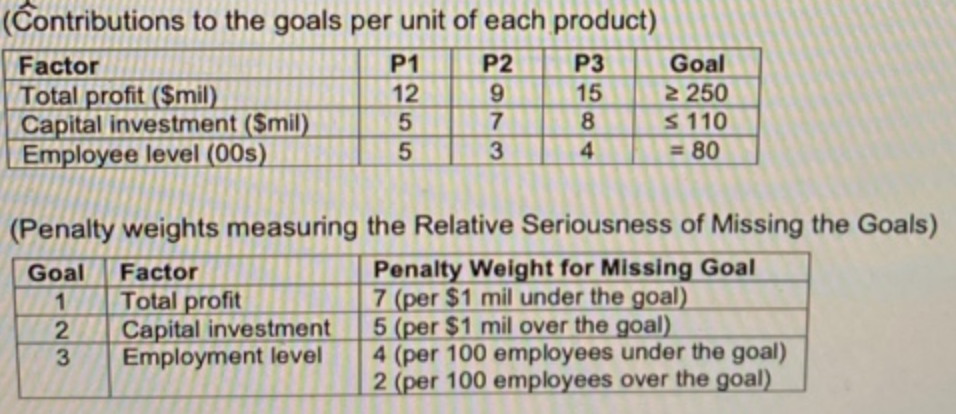
1. Formulate the above problem into Goal Programming (GP).
2. Find the optimal solution (Attach the Solver solution).
In: Operations Management
. Draw a diagram showing the demand and supply for aluminum in the United States. Assume...
. Draw a diagram showing the demand and supply for aluminum in the United States. Assume the United States can import as much as it wants at the world price of aluminum without causing the price to increase; and assume that the world price is lower than the U.S. equilibrium price. Be sure to indicate on your graph the quantity of aluminum imported. (Feel free to use hypothetical numbers.) Be sure to briefly describe your diagram in words.
2. Now show on your graph the effect of the U.S. imposing a tariff on aluminum. Be sure to indicate the new U.S. price, and the new quantity imported. (Again, feel free to use hypothetical numbers). Be sure to briefly describe your diagram in words.
3. Why would a tariff on aluminum be a “win” for American aluminum producers? Will anyone “lose” as a result of the tariff? Briefly explain using concepts from class.
In: Economics
According to a book published in 2011, 45% of the undergraduate students in the United States...
According to a book published in 2011, 45% of the undergraduate students in the United States show almost no gain in learning in their first two years of college (Richard Arum et al., Academically Adrift, University of Chicago Press, Chicago, 2011). A recent sample of 1460 undergraduate students showed that this percentage is 31%. Can you reject the null hypothesis at a 10% significance level in favor of the alternative that the percentage of undergraduate students in the United States who show almost no gain in learning in their first two years of college is currently lower than 45%. Use both the p-value and the critical-value approaches. Round your answers for the observed value of z and the critical value of z to two decimal places, and the p-value to four decimal places. zobserved =Enter you answer; z_observed Entry field with incorrect answer p-value =Enter you answer; p-valueEntry field with incorrect answer Critical value =Enter you answer; Critical valueEntry field with incorrect answer now contains modified data Hence we can conclude that the percentage of undergraduate students in the U.S. who show almost no gain in learning in their first two years of college is currently Choose the answer from the menu in accordance to the question statementEntry field with incorrect answer 45%.
In: Statistics and Probability
Select an ethnic minority group that is represented in the United States with respect to African...
Select an ethnic minority group that is represented in the United States with respect to African American Population only. Using health information available from Healthy People, the CDC, and other relevant government using health information available from Healthy People, the CDC, and other relevant government websites, analyze the health status for this group. In a paper of 1,000-1,250 words, compare and contrast the health status of your selected minority group to the national average. Include the following: 1) Describe the ethnic minority group selected. Describe the current health status of this group, that is African American Population. How do race and ethnicity influence health for this group? 2) What are the health disparities that exist for this group? What are the nutritional challenges for this group? 3) Discuss the barriers to health for this group resulting from culture, socioeconomics, education, and sociopolitical factors. 4) What health promotion activities are often practiced by this group? 5) Describe at least one approach using the three levels of health promotion prevention (primary, secondary, and tertiary) that is likely to be the most effective in a care plan given the unique needs of the minority group you have selected. Provide an explanation of why it might be the most effective choice. What cultural beliefs or practices must be considered when creating a care plan? 6) What cultural theory or model would be best to support culturally competent health promotion for this population? Why? Cite at least three peer-reviewed or scholarly sources to complete this assignment. Sources should be published within the last 5 years and appropriate for the assignment criteria and public health content.
In: Nursing
What is the definition of money in the United States? Does it correspond to what you...
What is the definition of money in the United States? Does it correspond to what you thought it was before you read Chapter 14? What are the benefits of fiat money?
https://www.federalreserve.gov/faqs/money_12845.htm (Links to an external site.)
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h6/current/default.htm
In: Economics
In a random sample of 765 adults in the United States, 322 say they could not...
In a random sample of 765 adults in the United States, 322 say they could not cover a $400 unexpected expense without borrowing money or going into debt.
A.)Find the mean and the standard deviation of p-hat for this sample
B.) Given the sample data in problem (1) above, construct a confidence interval at the 95% confidence level for the true proportion of Americans who could not cover a $400 unexpected expense without borrowing money or going into debt.
C.)4) Finding confidence intervals stems from getting a normal distribution of a sample proportion p-hat. If I estimate my population proportion to be no greater than 95%, what is the smallest sample size I can use to ensure I have a large enough sample to make a confidence interval?
Please help
In: Statistics and Probability
It appears that over the past 50 years, the number of farms in the United States...
It appears that over the past 50 years, the number of farms in the United States declined while the average size of farms increased. The following data provided by the U.S. Department of Agriculture show five-year interval data for U.S. farms. Use these data to develop the equation of a regression line to predict the average size of a farm (y) by the number of farms (x). Discuss the slope and y-intercept of the model.
| Year | Number of Farms (millions) | Average Size (acres) |
| 1960 | 5.69 | 218 |
| 1965 | 4.70 | 260 |
| 1970 | 3.91 | 298 |
| 1975 | 3.32 | 342 |
| 1980 | 2.95 | 372 |
| 1985 | 2.52 | 419 |
| 1990 | 2.47 | 426 |
| 1995 | 2.31 | 446 |
| 2000 | 2.16 | 459 |
| 2005 | 2.07 | 472 |
| 2010 | 2.18 | 433 |
| 2015 | 2.10 | 443 |
(Do not round the intermediate values. Round your
answers to 2 decimal places.)
y^= ______ +( _____ )x
In: Statistics and Probability
9. In 2018, 77% of the population of Netflix consumers in the United States had a...
9. In 2018, 77% of the population of Netflix consumers in the United States had a positive opinion of the
service. (remember, a percentage is a proportion x 100, so the population proportion here will be the
77/100)
a) What is the standard error of the sample proportion for a sample of 100 Netflix consumers? and of
200 Netflix consumers? (to 5 decimal places)
b) What is the probability that a random sample of 100 Netflix consumers will have a sample proportion
within 0.03 (
of the population proportion?
±
3%)
c) What is the probability that a random sample of 200 Netflix consumers will have a sample proportion
within 0.03 (
of the population proportion?
±
3%)
d) When sample size increases, we can see that the probability of getting a sample proportion close to
the true population proportion goes ___________ (
up/down
). So, as the sample size increases, point
estimators are likely to become _____________ (
more/less
) accurate.
In: Advanced Math
Rotelco is one of the largest digital wireless service providers in the United States. In a...
Rotelco is one of the largest digital wireless service providers in the United States. In a recent year, it had approximately 100 million direct subscribers (accounts) that generated revenue of $31,100 million. Costs and expenses for the year were as follows:
| Cost of revenue | $14,600 |
| Selling, general, and administrative expenses | 10,000 |
| Depreciation | 3,400 |
Assume that 70% of the cost of revenue and 30% of the selling, general, and administrative expenses are variable to the number of direct subscribers (accounts).
a. What is Rotelco's break-even number of
accounts, using the data and assumptions above? Round to the
nearest whole number.
million accounts
b. How much revenue per account would be
sufficient for Rotelco to break even if the number of accounts
remained constant? Round to the nearest dollar.
$ million per account
In: Accounting