Questions
Based on text book Management (Robbins S.) and Contemporary Engineering Economics (Chan Park). State 4 current...
In: Economics
Isle Royale, the islands of Cape Hatteras National Seashore, Nantucket, California's Channel Islands, and Elliott Key...
Isle Royale, the islands of Cape Hatteras National Seashore, Nantucket, California's Channel Islands, and Elliott Key in Biscayne National Park are all islands, but they all formed in different ways. Describe the different geological processes that created these different islands.
In: Other
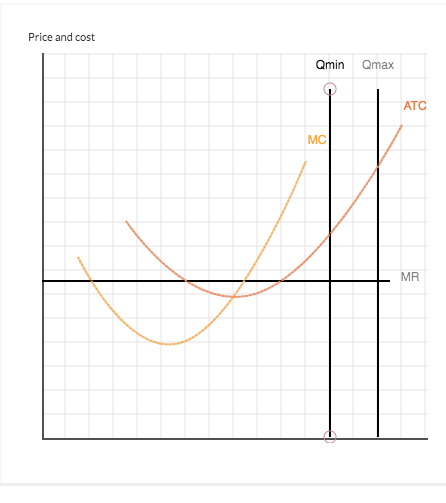
The graph below shows a particular firm's marginal revenue (MR), marginal cost (MC), and average total cost (ATC) curves
The graph below shows a particular firm's marginal revenue (MR), marginal cost (MC), and average total cost (ATC) curves, where the market is competitive. Suppose that a new management team is brought in and that this team is initially less concerned about maximizing profits than it is simply about making a profit. What range of production quantities will allow the firm to operate while earning a profit?
Give your answer by dragging the Qmin to Qmax lines into their correct positions. The output will need to lie somewhere betwen those limits.
To refer to the graphing tutorial for this question type, please click here.
In: Economics
Date Items Cost Total Cost March 1 10 $120 $1,200 March 4 13 $115 $1,495 March...
Date Items Cost Total Cost
March 1 10 $120 $1,200
March 4 13 $115 $1,495
March 16 20 $105 $2,100
March 28 18 $100 $1,800
Total 61 $6,595
During the month, 20 of the items were sold. Identify which cost flow assumption would achieve the indicated result.
Group of answer choices
Higher net income
FIFO Weighted-Average LIFO
Lower net income
FIFO Weighted-Average LIFO
Higher Inventory on the Balance Sheet
FIFO Weighted-Average LIFO
Lower Inventory on the Balance Sheet
FIFO Weighted-Average LIFO
In: Accounting
Hermione Co. reported the information shown in Table 5-1. Table 5-1 Units Unit Cost Total Cost...
Hermione Co. reported the information shown in Table 5-1.
Table 5-1
|
Units |
Unit Cost |
Total Cost |
Units Sold |
|
|
Beginning inventory (Jan. 1) |
4 |
$400 |
$1,600 |
|
|
Sale (Mar. 1) |
3 |
|||
|
Purchase (Apr. 15) |
4 |
405 |
1,620 |
|
|
Sale (June 22) |
3 |
|||
|
Purchase (Oct. 11) |
2 |
425 |
850 |
|
|
Total Units in ending inventory |
10 4 |
$4,070 |
6 |
10. Refer to Table 5-1. Assume that Hermione uses perpetual LIFO. The cost of the ending inventory is:
A. $1,700.
B. $1,670.
C. $1,655.
D. $1,600.
11. Refer to Table 5-1. Assume that Hermione uses perpetual weighted average costing. The average cost of a unit sold on June 22 is:
A. $400.
B. $402.50.
C. $404.
D. $405.
12. Refer to Table 5-1. Assume that Hermione uses perpetual FIFO. The entry to record the March 1 credit sale at a sale price of $800 per unit would include all of the following EXCEPT a:
A. credit to Inventory, $2,400.
B. debit to Cost of Goods Sold, $1,200.
C. debit to Accounts Receivable, $2,400.
D. credit to Sales Revenue, $2,400.
13. Refer to Table 5-1. Assume that Hermione uses periodic FIFO. The cost of goods sold for the period is:
A. $2,470.
B. $2.410.
C. $1,660.
D. $1,600.
In: Accounting
Support-department cost allocations: single-department cost pools; direct, step-down, and reciprocal methods. 1 a. Allocate the total...
| Support-department cost allocations: single-department cost pools; direct, step-down, and reciprocal methods. | |||||
| 1 | a. | Allocate the total Support Department costs to the production departments under the Direct Allocation Method: | |||
| Clothing | Shoes | ||||
| Departmental Costs | $10,500 | $7,500 | |||
| From: | |||||
| Information Technology | |||||
| (5040/9000)*2600 | $1,456 | ||||
| (3960/9000)*2600 | $1,144 | ||||
| Human Resources | |||||
| (220/308)*1400 | $1,000 | ||||
| (22/308)*1400 | $400 | ||||
| Total Departmental Costs | $12,956 | $9,044 | |||
| Total Costs to account for: | $ 22,000 | ||||
| b. | Allocate the Support Department Costs to the Production Department under the Step-down (Sequential) Allocation Method IT first sequentially: | ||||
| To: | |||||
| IT | HR | Clothing | Shoes | ||
| Departmental Costs | $2,600 | $1,400 | $10,500 | $7,500 | |
| From: | |||||
| Information Technology | -$2,600 | ||||
| (3000/12000)*2600 | $650 | ||||
| (5040/12000)*2600 | $1,092 | ||||
| (3960/12000)*2600 | $858 | ||||
| Human Resources | -$2,050 | ||||
| (220/308)*2050 | $1,464 | ||||
| (88/308)*2050 | $586 | ||||
| Total Departmental Costs | $0 | $0 | $13,056 | $8,944 | |
| Total Costs to account for: | $ 22,000 | ||||
| c. | Allocate the Support Department Costs to the Production Department under the Step-down (Sequential) Allocation Method HR first sequentially: | ||||
| To: | |||||
| HR | IT | Clothing | Shoes | ||
| Departmental Costs | $1,400 | $2,600 | $10,500 | $7,500 | |
| From: | |||||
| Human Resources | -$1,400 | ||||
| (92/400) _ $1,400 | $322 | ||||
| (220/400) _ $1,400 | $770 | ||||
| (88/400) _ $1,400 | $308 | ||||
| Information Technology | -$2,922 | ||||
| (5,040/9,000) _ $2,922 | $1,636 | ||||
| (3,960/9,000) _ $2,922 | $1,286 | ||||
| Total Departmental Costs | $0 | $0 | $12,906 | $9,094 | |
| Total Costs to account for: | $ 22,000 | ||||
| d. | Allocate the Support Department Costs to the Production Department under the Reciprocal Allocation Method: | ||||
| i. Assign reciprocal equations to the support departments | |||||
| IT=(2600+92 employees/400 employees*HR) | |||||
| IT = | $2,600+0.23HR | ||||
| HR = | ($1,400+.025 IT) | ||||
| HR=($1,400+3,000 hours/1,200 hours IT) | |||||
| ii. Solve the equation to complete the reciprocal costs of the support departments | |||||
| IT=$2,600+.023($1,400+0.25 IT) | |||||
| IT= $2,600+$322+0.0575IT | |||||
| 0.9425 IT = $2,922 | |||||
| IT = | $ 3,100 | ||||
| HR= $1,400+0.25 IT | |||||
| HR= $1,400+0.25(3,100) | |||||
| HR= $1,400+775 | |||||
| HR = | $2,175 | ||||
| iii. Allocate Reciprocal costs to departments (all numbers rounded to nearest dollar) | |||||
| IT | HR | Clothing | Shoes | ||
| Departmental Costs | $2,600 | $1,400 | $10,500 | $7,500 | |
| Information Technology | -$3,100 | ||||
| (3000/12000)*$3,100 | $775 | ||||
| (5040/12000)*$3,100 | $1,302 | ||||
| (3960/12000)*$3,100 | $1,023 | ||||
| Human Resources | -$2,175 | ||||
| (92/400)*$2,175 | $500 | ||||
| (220/400)*$2,175 | $1,196 | ||||
| (88/400)*$2,175 | $479 | ||||
| Total Departmental Costs | $0 | $0 | $12,998 | $9,002 | |
| $ 22,000 | |||||
| Reciprocal Method of Allocating Support Department Costs for Sportz, Inc. Using Repeated Iterations. | |||||
| Support Departments | Operating Departments | ||||
| IT | HR | Clothing | Shoes | ||
| Budgeted manufacturing overhead costs before any interdepartmental cost allocations | |||||
| 1st Allocation of IT Dept. | |||||
| (0.25, 0.42, 0.33)b | |||||
| 1st Allocation of HR Dept. | |||||
| 2nd Allocation of IT Dept. | |||||
| 2nd Allocation of HR Dept. | |||||
| 3rd Allocation of IT Dept. | |||||
| 3rd Allocation of HR Dept. | |||||
| 4th Allocation of IT Dept. | |||||
| Total budgeted manufacturing | |||||
| overhead of operating departments | |||||
I understand the first half just not the both half.
Sportz, Inc., manufactures athletic shoes and athletic clothing for both amateur and professional athletes. The company has two product lines (clothing and shoes), which are produced in separate manufacturing facilities; however, both manufacturing facilities share the same support services for information technology and human resources. The following shows total costs for each manufacturing facility and for each support department.
| Variable Costs | Fixed Costs | Total Costs by Department | ||
| Information Technology | 600 | 2,000 | 2,600 | |
| Human Resources | 400 | 1,000 | 1,400 | |
| Clothing | 2,500 | 8,000 | 10,500 | |
| Shoes | 3,000 | 4,500 | 7,500 | |
| Total Costs | 6,500 | 15,500 | 22,000 |
The total costs of the support departments (IT and HR) are allocated to the production departments (clothing and shoes) using a single rate based on the following:
Information technology: Number of IT labor-hours worked by
department
Human resources: Number of employees supported by department
Data on the bases, by department, are given as follows:
|
Department |
IT Hours Used |
Number of Employees |
||
|
Clothing |
5,040 |
220 |
||
|
Shoes |
3,960 |
88 |
||
|
Information technology |
- |
92 |
||
|
Human resources |
3,000 |
- |
What are the total costs of the production departments (clothing and shoes) after the support department costs of information technology and human resources have been allocated using (a) the direct method, (b) the step-down method (allocate information technology first), (c) the step-down method (allocate human resources first), and (d) the reciprocal method?
Assume that all of the work of the IT department could be outsourced to an independent company for $97.50 per hour. If Sportz no longer operated its own IT department, 30% of the fixed costs of the IT department could be eliminated. Should Sportz outsource its IT services?
In: Accounting
Units Per unit cost Total cost 5,000 units 5000 17.00 85000 7,500 units 7500 13.00 97500...
| Units | Per unit cost | Total cost | |
| 5,000 units | 5000 | 17.00 | 85000 |
| 7,500 units | 7500 | 13.00 | 97500 |
| Difference | 2500 | 12500 | |
| Unit variable cost | 5 | =12500/2500 | |
| Fixed cost | 60000 | =85000-(5000*5) | |
| Y = $60,000 + $5X |
what is that X suppose to mean ?is the answer 60,005?
In: Accounting
Which product costing system distributes costs evenly across total production? Variable cost system Standard cost system...
Which product costing system distributes costs evenly across total production?
Variable cost system
Standard cost system
Process cost system
Job order cost system
In: Accounting
Date Explanation Units Unit Cost Total Cost June 1 Inventory 180 5 900 12 Purchase 285...
| Date | Explanation | Units | Unit Cost | Total Cost |
| June 1 | Inventory | 180 | 5 | 900 |
| 12 |
Purchase |
285 | 6 | 1710 |
| 23 | Purchase | 535 | 7 | 3745 |
| 30 | Inventory | 175 |
Compute the cost of the ending inventory and the cost of goods sold under FIFO and average-cost.
In: Accounting
A random group of thirty customers at a local theater was interviewed regarding their movie viewing habits.
A random group of thirty customers at a local theater was interviewed regarding their movie viewing habits. The following responses were obtained for the question, “How many times during the past month did you go to the movies?” Number of movies attended 0 1 2 3 4 Number of customers 3 10 8 6 3 a. b. Find the probability that a customer selected at random went to the movies:
1) more than one time, 2) two times, 3) at least two times, 4) no more than three times.
In: Statistics and Probability